Figure 2.
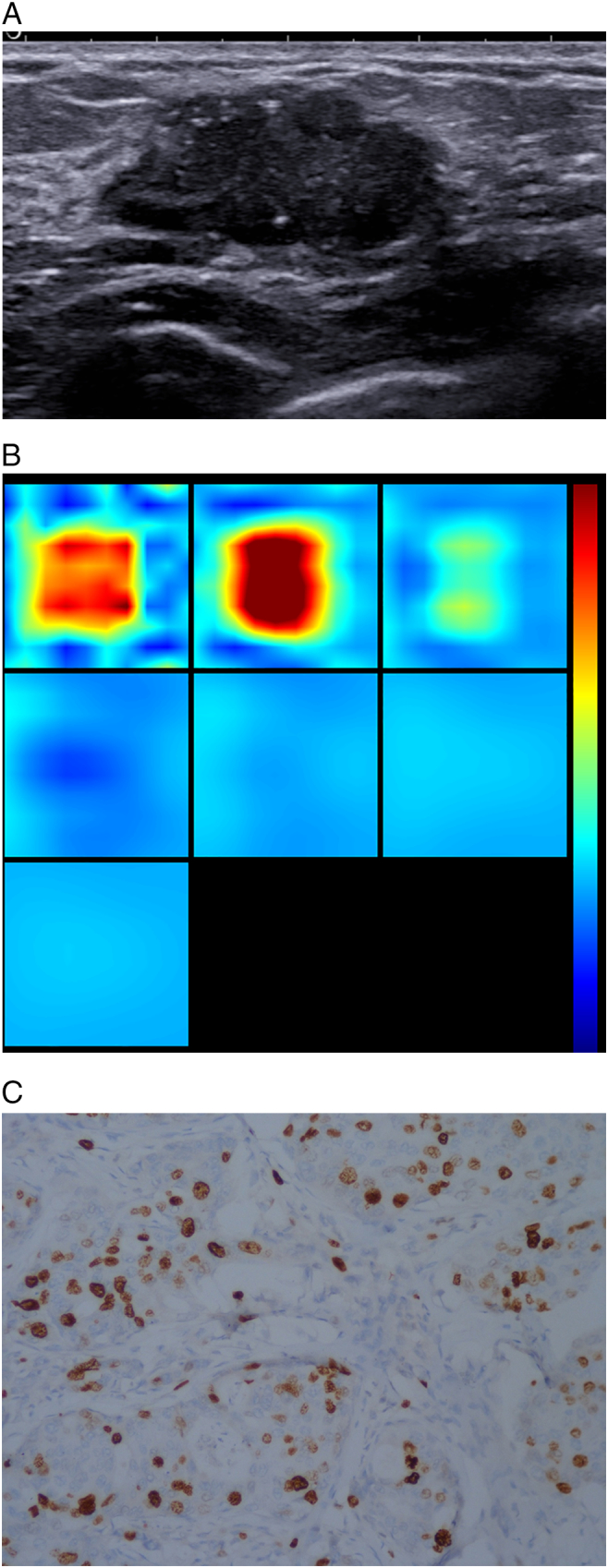
Patient age 44y, currently in the Menstrual Phase, BMI21.7, pathology diagnosis of invasive ductal breast cancer, immunohistochemistry: ER+, PR+, HER +, KI67 20%, LN-, LVI-.
(A). US 2-D imaging showing hypoechoic lesion, maximal diameter of 27 × 14 × 25 mm, irregular shape, with no circumscribed margin, a few hyperechoic spots close to lesion edge, lesion edge-nipple distance 27 mm, lesion edge-skin surface distance 4 mm.
(B). A reconstructed optical absorption maps show that the lesion is resolved in slices from 1 to 3 (top row, left to right). THCmean is 244.8 μmol/L. The first section (slice 1, top left) is a 6 × 6 cm spatial x–y image (coronal plane of the body) obtained at a depth of 0.5 cm, as measured from the skin surface. The last section (slice 7, bottom left) is a 6 × 6 cm spatial x–y image (coronal plane of the body) obtained at a depth of 3.5 cm towards the chest wall. Spacing between sections is 0.5 cm in the direction of propagation. The vertical color scale from blue to red is the THC in micromoles per liter from low to high.
(C). Ki-67 nuclear staining (×200). The Ki-67 proliferation index is determined as 20%.
