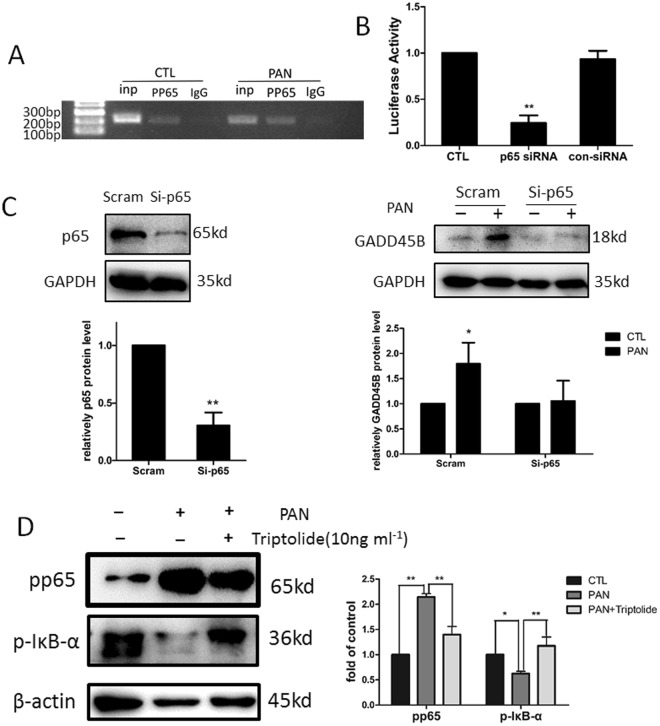
Figure 7.
Triptolide downregulates GADD45B expression via inhibition of NF-κB signalling. (A) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analysis in podocytes using an antibody to phospho-NF-κB p65, followed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using the GADD45B gene promoter-specific primer. The amplified sequence is designed +255 to +455 base pairs downstream of the transcription start site (chr19: 2476721-2476731). More NF-κB p65 bound directly to the GADD45B promoter region after exposure to PAN for 24 h compared to normal control. (B) The luciferase assay confirmed that GADD45B promoter activity was significantly decreased by inhibition of NF-κB p65. (C) Human podocytes transfected with NF-κB p65 siRNA and scramble control for 48 h followed by PAN stimulation (50 µg ml−1) for 12 h. NF-κB p65 knockdown prevented PAN-induced upregulation of GADD45B. (D) Human podocytes were incubated with 50 µg ml−1 PAN and 10 ng ml−1 triptolide for 6 h, and immunoblotting shows a marked reduction in NF-κB activity in the podocytes treated with triptolide and PAN compared to podocytes treated with PAN only. (n = 3). **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05. Each blot was cropped at the position of the blotted protein, and high-contrast was not used.