FIGURE 3.
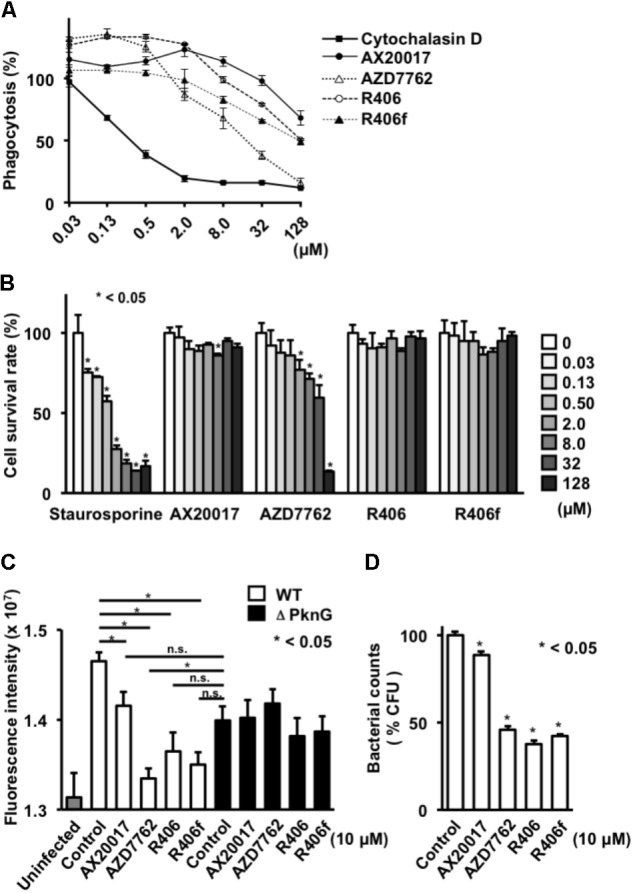
Effect of PknG inhibitors on phagocytosis, cell viability, and intracellular survival of bacteria in human macrophage. (A) Phagocytotic activity of differentiated THP-1 cells. Cells were incubated with fourfold serial dilutions of each compound from 0.03 to 128 mM for 2 h. Opsonized beads containing the same concentration of the test compound were added at an MOI of 10 and cultured. The fluorescence intensity was measured after 2 h. (B) Cytotoxicity of each compound. Serially diluted compound was added to the differentiated THP-1 cells. MTT assay was performed after 24 h. (C) Survival of mycobacteria in human macrophage after treatment with PknG inhibitors. THP-1 macrophages infected with WT BCG or ΔPknG BCG were treated with 10 μM of each compound. After 2 h incubation, infected macrophages were washed and incubated with amikacin (20 μM) in the presence of inhibitors. And each compound (10 μM) was added for another 24 h at 37°C. The macrophages were washed, lysed, and added with 20 μL of alamarBlue reagent. The mixtures were incubated for 12 h at 37°C. Fluorescence intensity of WT BCG (white bar), ΔPknG BCG (black bar), and null (gray bar) infected macrophages were measured. (D) Effect of PknG inhibitors on survival of mycobacteria in macrophages. Human THP-1 macrophages infected with BCG were treated with 10 μM of each compound. Infected THP-1 cells were lysed and serially diluted. A total of 10 μl of each diluent were spotted onto an agar plate. After incubation of the plates, the emerged bacterial colonies were counted. ∗P < 0.05. WT: WT BCG, ΔPknG: ΔPknG BCG, control: medium alone, R406f: R406-free base.
