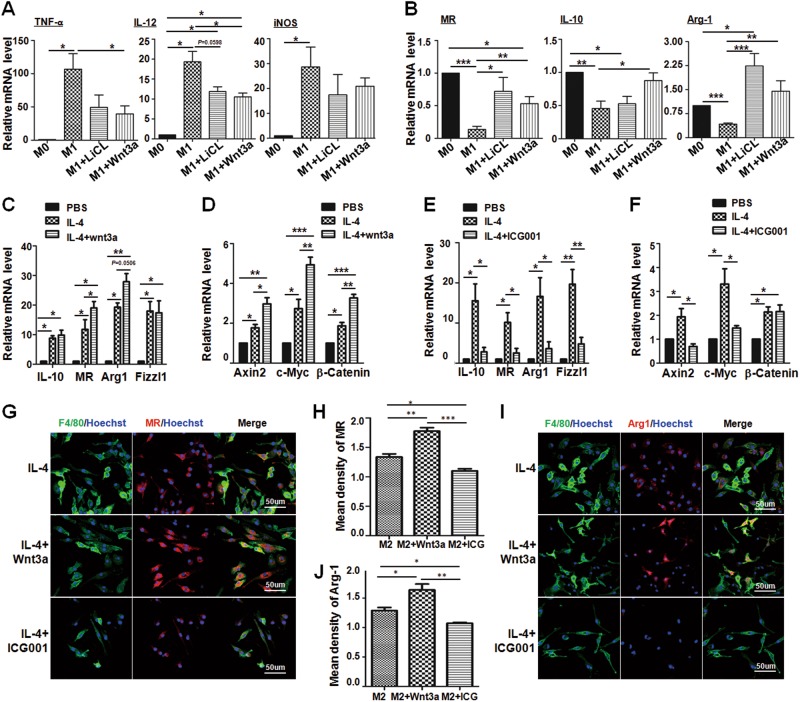
Fig. 2. Wnt/β-catenin signaling activation promotes M2 macrophages polarization.
a, b BMDMs (M0) were treated with Wnt3a (100 ng/mL) or LiCl (10 mM) in advance. Cells were then stimulated with LPS + IFN-γ (M1) for 24 h. The mRNA levels of M1 markers such as TNF-α, IL-12, and iNOS (a), and M2 markers, including Arg1, MR and IL-10 (b), were determined by qRT-PCR, respectively. β-actin was used as an internal control (n = 3). c, d BMDMs were polarized with IL-4 (M2) followed by Wnt3a (100 ng/mL) treatment or no treatment for 24 h. The mRNA level of M2 markers (c) and the downstream genes of Wnt signaling (d) were detected by qRT-PCR, and then were quantitatively compared (n = 3). e, f Wnt signaling inhibitor ICG001 (10 μM) was added into BMDMs, and then BMDMs were polarized with IL-4 for 24 h. The mRNA level of M2 markers (e) and the downstream genes of Wnt signaling (f) were examined by qRT-PCR, and then compared quantitatively (n = 3). g−j BMDMs were cultured on coverslips, and treated with Wnt3a or ICG001 followed by IL-4 stimulation for 24 h. Then cells were subjected to IF staining using anti-F4/80 and anti-MR (g, h) or anti-Arg1 (i, j) antibodies. Nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst (n = 3). Mean florescence intensity was determined and compared. Bars, mean ± SD; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001