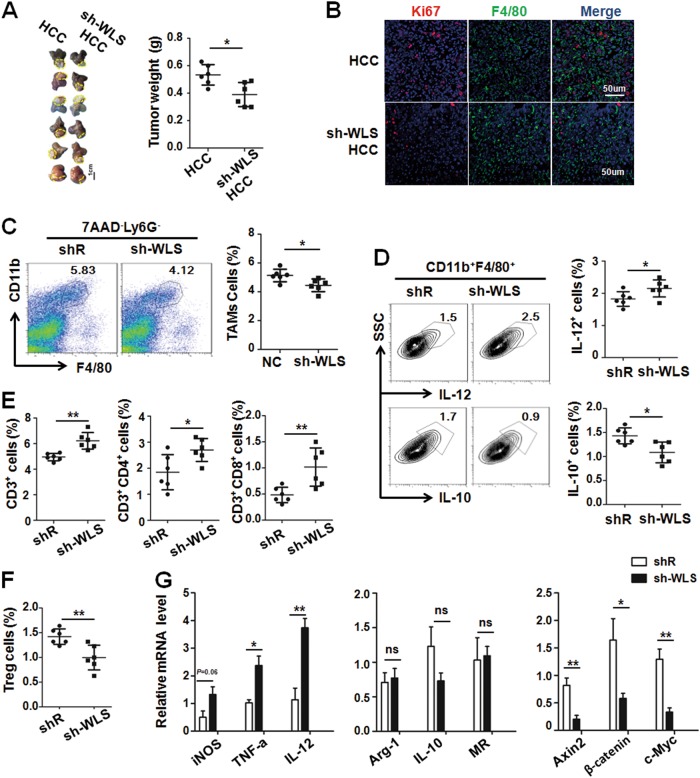
Fig. 6. Knockdown Wntless in Hepa1-6 cells inhibited tumor growth by reducing M2-like TAMs and increasing antitumor T cells.
a Infected Hepa1-6 cells as described in Supplement Fig. 2C were orthotopically inoculated in the liver of C57BL/6 mice. Tumors were dissected 3 weeks after inoculation and photographed (left panel). Tumor weight was compared (right panel) (n = 6). b Tumor sections were stained with anti-F4/80 and Ki67 using immunofluoresecence staining. Ki67+ cells were counted and compared (n = 3). c Single cells suspensions from tumor tissues in (a) were prepared and stained. The Ly6G-F4/80+ CD11b+cells (TAMs) were analyzed by FACS. The percentage of TAMs cells in tumor tissue were compared (n = 6). d Tumor single cell suspension was analyzed by FACS for detecting the cytoplasmic IL-10 and IL-12 expression in TAMs. The percentage of IL-12+ TAMs and IL-10+TAMs was compared (n = 6). e The percentage of CD3+ cells, CD3+CD4+cells and CD3+CD8+ cells in tumor cell suspensions were analyzed by FACS and then compared (n = 6). f The percentage of CD4+FoxP3+CD25+ cells (Treg) cells was analyzed by FACS and then compared (n = 6). g TAMs were sorted from liver of hepatic tumor-bearing mice or sh-WLS infected hepatic tumor-bearing mice, and then the M1/M2-polarized markers and the downstream genes of Wnt/β-catenin signaling were determined by qRT-PCR and quantitatively compared (n = 4). Bars, mean ± SD; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01