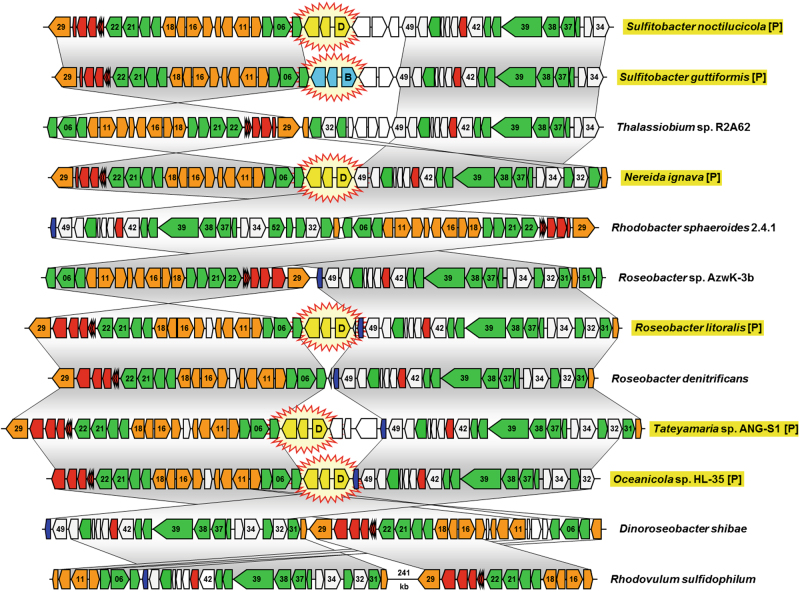
Fig. 3.
Comparison of six plasmid-located and six chromosomal photosynthesis gene clusters from Rhodobacteraceae. Selection of 12 among the 48 PGCs that were analyzed in the current study (see Tab. S4). Genes are colored according to biological categories: green, bacteriochlorophyll biosynthesis (bch); orange, carotenoid biosynthesis (crt); red, light-harvesting and photosynthesis reaction center (puf); dark blue, cytochrome c2 (cycA); gray, additional conserved genes of the PGC; white, non-conserved genes. The positioning of plasmid modules in the photosynthesis gene cluster, which are shown in yellow (DnaA-like I) and light blue (RepB-III), is highlighted by star-shaped icons. Identical gene order between PGCs is indicated by vertical gray shaded areas. Two conserved parts of the chromosomal PGC from Rhodovulum sulfidophilum are separated by a DNA stretch of 241-kb. Plasmid-located PGCs are highlighted in yellow and by the suffix [P] (color figure online)