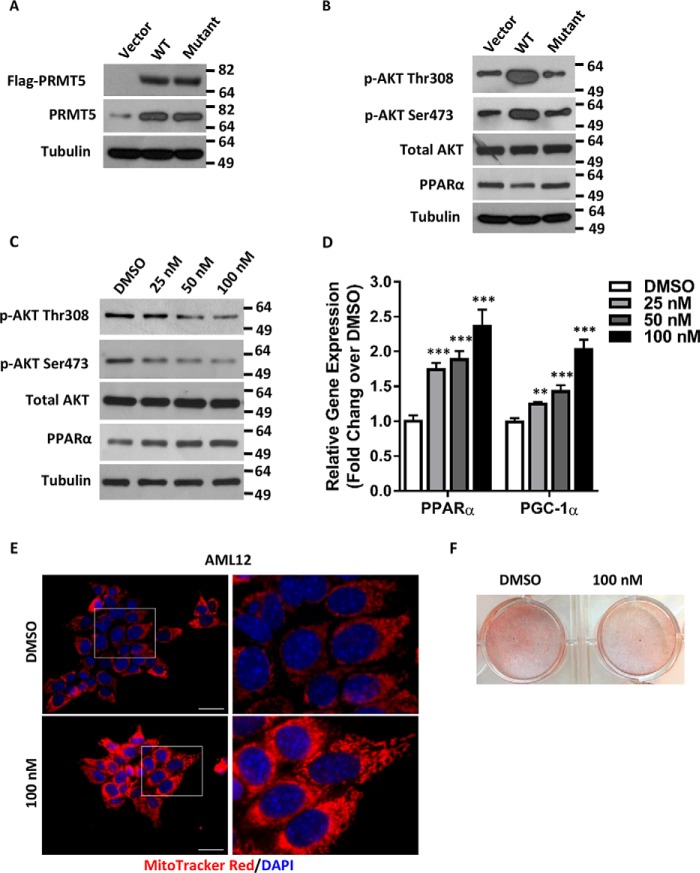
Figure 5.
PRMT5 enzymatic activity is required for its regulation of PPARα expression. A, a FLAG-tagged WT or enzyme-dead (G367A,R368A) double PRMT5 mutant was introduced to AML12 cells by transient transfection. The expression of exogenous proteins was examined by Western blot analysis using anti-FLAG antibody. The total levels of PRMT5 were measured by Western blotting against anti-PRMT5 antibody. B, AKT phosphorylation and expression of PPARα in WT or mutant PRMT5-expressing cells were analyzed by Western blotting. C, protein levels of phospho-AKT and PPARα were determined by Western blotting in AML12 cells treated with DMSO or increasing doses of the PRMT5 inhibitor EPZ015666. D, the relative mRNA of PPARα and PGC-1α was measured by qRT-PCR in AML12 cells treated with DMSO or increasing doses of EPZ015666. E, AML12 cells treated with DMSO or 100 nm EPZ015666 were stained by MitoTrackerTM Red CMXRos (red), and nuclei were labeled with DAPI (blue). Scale bars = 200 μm. ***, p < 0.001; two-tailed Student's t test. F, AML12 cells pretreated with DMSO or 100 nm EPZ015666 were exposed to medium containing 1 μm palmitic acid and 100 μm oleic acid for 5 days. Intracellular lipids were stained with Oil Red O.