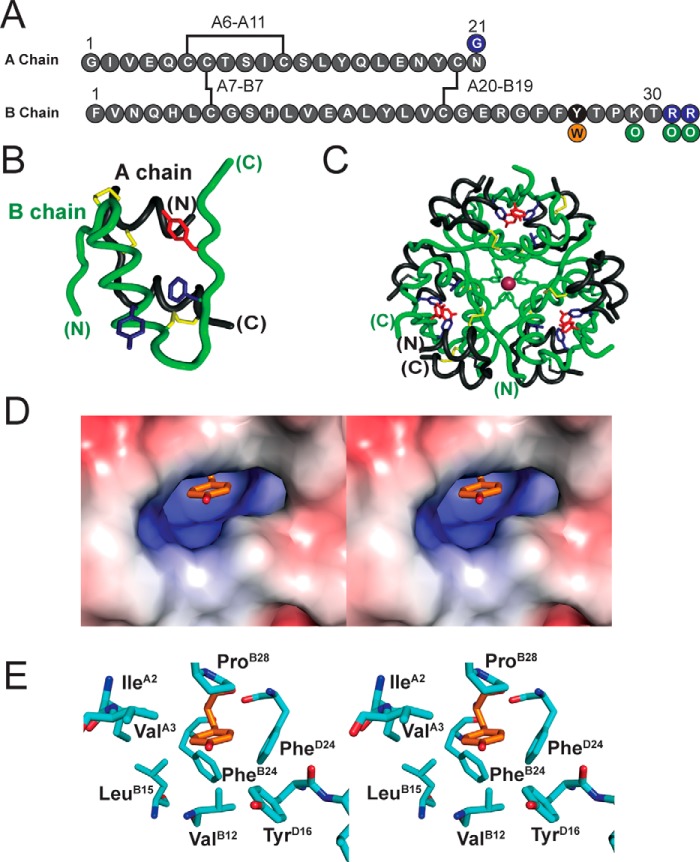
Figure 1.
Structural overview of insulin. A, sequence of insulin with disulfide bridges in black. TyrB26 is highlighted in black; the present TyrB26 → Trp substitution is orange; and modifications in pI-shifted clinical analog glargine in purple. Our semisynthetic pI-shifted analog contained Orn (green) instead of Lys or Arg. B, structure of an insulin monomer; the A chain is shown in black and B chain in green. TyrB26 is red, whereas PheB24 and TyrB16 are blue (PDB code 4INS). C, structure of zinc-coordinated insulin hexamer (T6 state), a trimer of dimers; TyrB26, PheB24, and TyrB16 are color-coded as in B. D, stereo view showing TyrB26 (sticks) in a cavity within insulin dimer (extracted from T3Rf3 hexamer, PDB code 1TRZ). E, corresponding stick model with residues labeled.