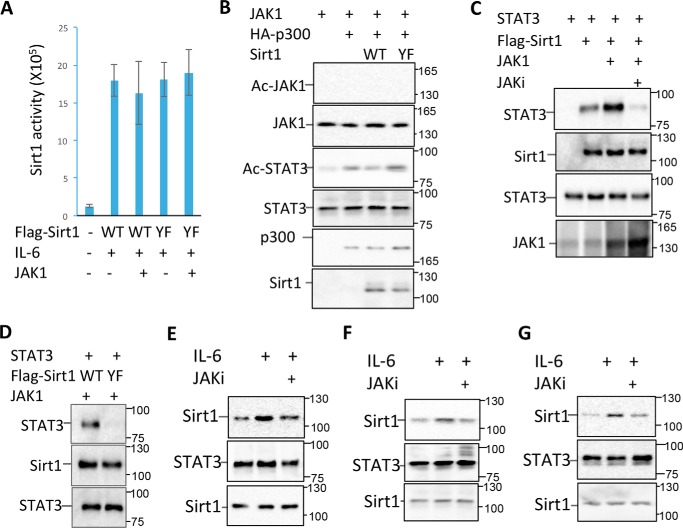
Figure 3.
Sirt1 tyrosine phosphorylation enhances its interaction with STAT3. A, JAK1 expression plasmid was transfected into MCF-10 cells with either FLAG-Sirt1 or FLAG-Sirt1/YF mutant. Two days after the transfected cells were treated with or without IL-6 for 30 min and lysed. Sirt1 was immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibody, the deacetylase activity of Sirt1 was determined. Error bars represent data from three independent experiments. B, JAK1 and STAT3 were co-expressed with p300 and Sirt1 or its YF mutant in the MCF-10 cells as indicated. JAK1 acetylation was determined by immunoprecipitation of JAK1 and Western blotting with anti–acetyl-lysine Abs (top panel). The same membrane was reprobed with anti-JAK1 (second panel). STAT3 acetylation was determined by immunoprecipitation of STAT3 and by Western blotting with anti–acetyl-lysine Abs (third panel). The same membrane was reprobed with anti-STAT3 (fourth panel). The expression levels of p300 and Sirt1 in the whole cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting (bottom two panels). C, STAT3, JAK1, and Sirt1 expression plasmids were transfected into MCF-10 cells as indicated. The transfected cells were treated with the JAK inhibitor PF-04965842 and then collected. STAT3 interaction with Sirt1 was determined by immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG antibody and Western blotting with anti-STAT3 (top panel). The same membrane was reprobed with anti-Sirt1 (second panel). The expression levels of STAT3 (third panel) and JAK1 (bottom panel) in the whole cell lysates were determined by Western blotting. D, MCF-10 cells were transfected with STAT3, JAK1, and Sirt1 or its YF mutant. The interaction of STAT3 with Sirt1 in the lysate of treated cells was determined as in (C). E–G, MCF-10 (E), HCT116 (F), and MM.1s (G) cells were stimulated with or without IL-6 or further with JAK1 inhibitor PF-04965842 (1 μm), and then lysed with RIPA buffer. Sirt1 interaction with STAT3 was determined as in (C).