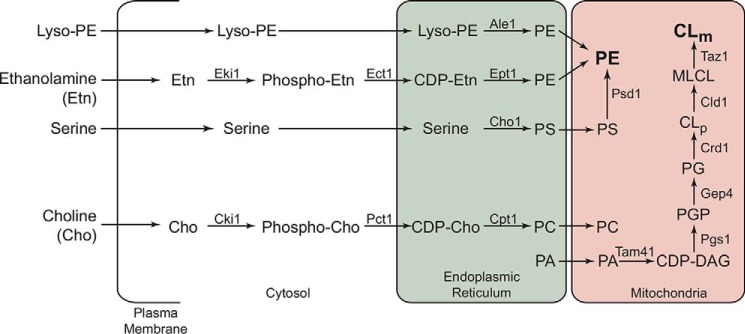
Figure 1.
Biochemical pathways for PE, PC, and CL biosynthesis in the yeast S. cerevisiae. CL biosynthesis occurs exclusively in the mitochondria, where Crd1 synthesizes nascent CLp from PG. The resulting CLp is deacylated by the phospholipase Cld1 to produce monolysocardiolipin (MLCL), which is then reacylated by the transacylase Taz1 to form mature cardiolipin (CLm). Mutations in the human homologue of TAZ1 result in Barth syndrome. CL biosynthesis depends on the import of PA from endoplasmic reticulum, which is converted to CDP-DAG by Tam41. Pgs1 catalyzes conversion of CDP-DAG to PGP, which is then dephosphorylated to PG by Gep4. PE biosynthesis in yeast can occur by the following: 1) Psd1-catalyzed decarboxylation of PS in the mitochondria; 2) incorporation of Etn via the cytosolic/endoplasmic reticulum Kennedy pathway enzymes Eki1, Ect1, and Ept1, respectively; and 3) the acylation of lyso-PE by Ale1. The Kennedy pathway enzymes Cki1, Pct1, and Cpt1 can utilize choline to biosynthesize PC, a bilayer-forming phospholipid that is imported into mitochondria. CLp, precursor cardiolipin; CLm, mature cardiolipin; PG, phosphatidylglycerol; PGP, phosphatidylglycerol phosphate; CDP, cytidine diphosphate; DAG, diacylglycerol.