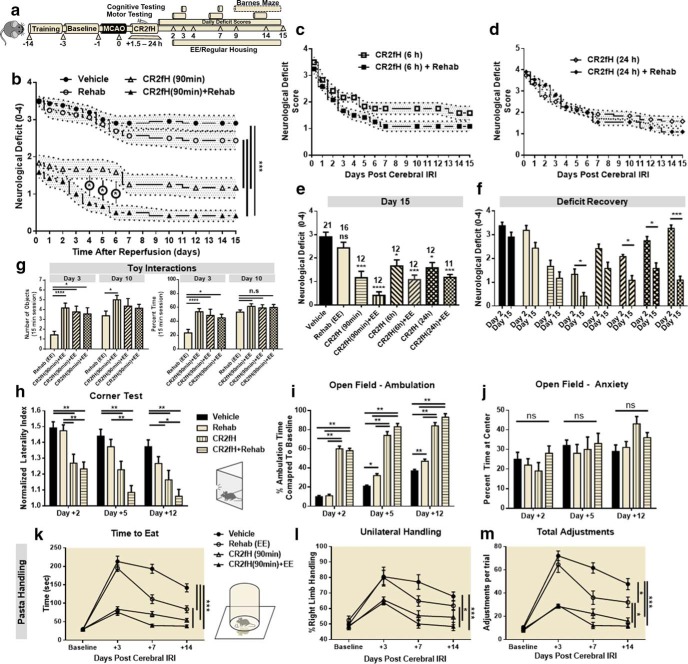
Figure 3.
Combination of CR2fH treatment and rehabilitation therapy resulted in faster and more pronounced motor recovery 15 d after MCAO. a, Overview of the experimental design. Survival curve for different groups is shown in Figure 1h. b, CR2fH administered 90 min after ischemia with or without rehabilitation resulted in significant and sustained improvement in neurological deficit over 15 d of recovery compared with vehicle or rehabilitation therapy alone. Compared with CR2fH alone, the CR2fH + rehabilitation group exhibited significantly faster recovery during the first week after MCAO. Two-way ANOVA, Bonferroni's correction, n = 11–21/group (individual n's are shown in Fig. 2e). *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001. c, d, CR2fH also improved recovery of functional deficits when administered 6 h (c) or 24 h (d) after MCAO. e, Comparison of neurological deficits at day 15 after injury showing that CR2fH significantly improved long-term functional recovery compared with vehicle and that, when combined with rehabilitation, more pronounced recovery is observed. Comparisons were made against vehicle group. Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn's multiple comparisons, not significant (ns), *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. f, Pairwise comparison of functional recovery between days 2 and 15 across the different groups showing that, despite significant acute improvement achieved with CR2fH alone compared with vehicle, combination of CR2fH with rehabilitation, but not CR2fH or rehabilitation alone, resulted in more pronounced recovery beyond the acute phase (between days 2 and 15). Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's correction, n = 11–21/group, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001. g, Among animals treated with rehabilitation, animals cotreated with CR2fH showed significantly more interaction with the enriched environment compared with vehicle-treated animals at day 3, but not day 10, after MCAO. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's correction, n = 16 vehicle, n = 12 CR2fH 90 min, n = 7 CR2fH 6 and 24 h, *p < 0.05.***p < 0.001. h, i, During the first week of recovery, CR2fH (90 min) alone or with rehabilitation significantly reduced forelimb asymmetry on the corner test (h) and increased open-field locomotor activity (i) compared with vehicle. Combination treatment has the largest effect on both tasks at any time point. j. No difference among groups was seen in the percentage time spent at center, thus controlling for potential difference in anxiety levels between the groups. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's correction, n = 21 vehicle, n = 16 rehabilitation, n = 12 CR2fH ± rehabilitation, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. k–m, On pasta-handling task, animals treated with rehabilitation, CR2fH, or CR2fH + rehabilitation showed signs of improvement in time to eat compared with vehicle (k), but the improvement in unilateral handling and number of adjustments was only significant in CR2fH ± rehabilitation animals compared with vehicle controls. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's correction, n = 8/group, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.