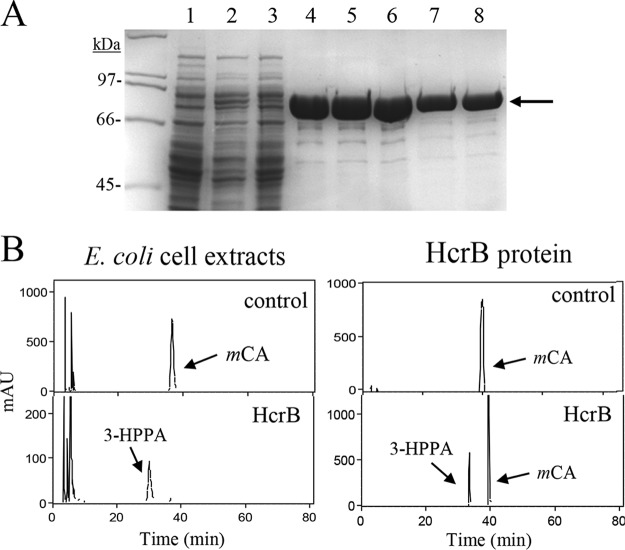
FIG 4.
Purification and enzymatic activity of E. coli extracts expressing L. plantarum HcrB and recombinant HcrB protein. (A) SDS-PAGE analysis of the expression and purification of the His6-tagged HcrB. Results of analysis of soluble cell extracts of IPTG-induced E. coli BL21(DE3)(pURI3-Cter) (lane 1) or E. coli BL21(DE3)(pURI3-Cter-HcrB) (lane 2), flowthrough from the affinity resin (lane 3), and fractions eluted from His affinity resin (lanes 4 to 8). The 8% gel was stained with Coomassie blue. Molecular mass markers are located on the left (SDS-PAGE standards; Bio-Rad). (B) HPLC chromatograms showing hydroxycinnamate reductase activity of soluble cell extracts of IPTG-induced E. coli BL21(DE3)(pURI3-Cter) (control) or E. coli BL21(DE3)(pURI3-Cter-HcrB) (HcrB) incubated in 1.5 mM m-coumaric acid. HPLC chromatograms also showed the reductase activity of purified His6-HcrB protein (500 μg) (HcrB) or without protein (control). The m-coumaric acid (mCA) and 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)propionic acid (3-HPPA) detected are indicated. Chromatograms were recorded at 280 nm.