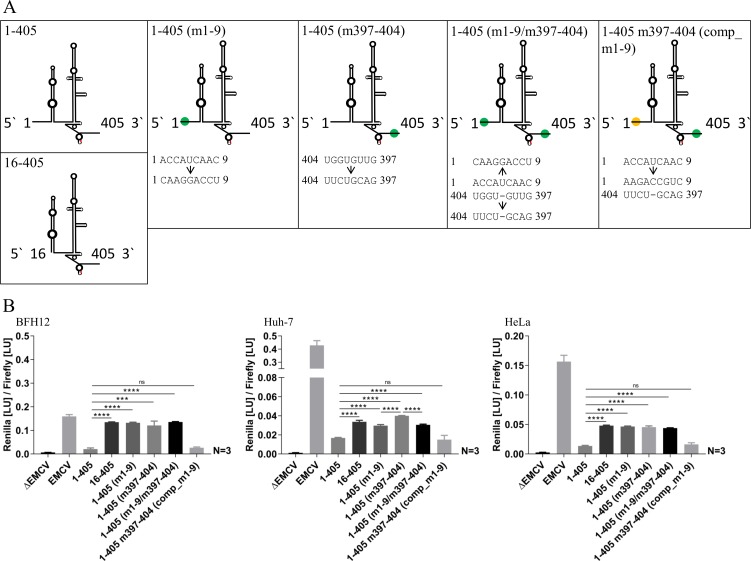
FIG 4.
(A) Schematic diagrams of investigated BovHepV 5′ NTR secondary structures and mutations on the nucleotide level. Red, translation initiation codon (AUG); green and yellow dots, mutated regions in the 5′ NTR and the core coding sequence. (B) Luciferase activities at 48 h posttransfection in BFH12, Huh-7, and HeLa cells. Plasmid pF/R_EMCV (EMCV) was used as a positive control, and plasmid without the EMCV IRES sequence (ΔEMCV) was used as a negative control. The following plasmids with different partial sequences of BovHepV were transfected: 1-405, virus sequence from nt 1 to 405 (including 111 nt of the core coding sequence); 16-405, BovHepV sequence starting from domain II up to nt 405; 1-405 (m1-9), BovHepV sequence from nt 1 to 405 with mutated IRES sequence (nt 1 to 9); 1-405 (m397-404), BovHepV sequence from nt 1 to 405 with mutated IRES sequence (nt 397 to 404); 1-405 (m1-9/m397-404), BovHepV sequence from nt 1 to 405 containing mutated IRES sequence information at two sites (nt 1 to 9 and nt 397 to 404); 1-405 m397-404 (comp_m1-9), BovHepV sequence from nt 1 to 405 with mutated IRES sequence (nt 397 to 404), which contains additional compensatory mutations of nt 1 to 9. For enhanced illustration of the results, uniform scaling was not used in panel B. EMCV, encephalomyocarditis virus IRES sequence; NTR, nontranslated region.