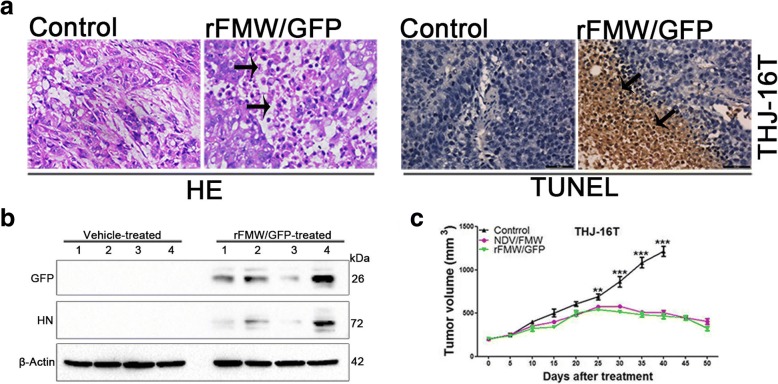
Fig. 5.
In vivo antitumor effects of rFMW/GFP. a One week after treatment, tumor tissue samples from four different animals from each treatment group (of eight) were subjected to either hematoxylin-eosin (H&E) staining (Tumor necrosis indicated by the arrows) or TUNEL assay (Arrowheads indicate brown 3,3′-diaminobenzidine chromogen in cell nuclei) or b immunoblot analysis of GFP and HN expression. β-actin was used as a loading control. Scale bar = 50 μm. c Mice were treated as described above for 3 weeks. Tumor volumes were measured at 5-day intervals for 50 days after injections and expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 10) in tumor volume-time curves. Differences in tumor regression were significant between virus-treated and vehicle control groups. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM and are representative of two independent experiments (0.001 < **p < 0.005; ***p < 0.0001)