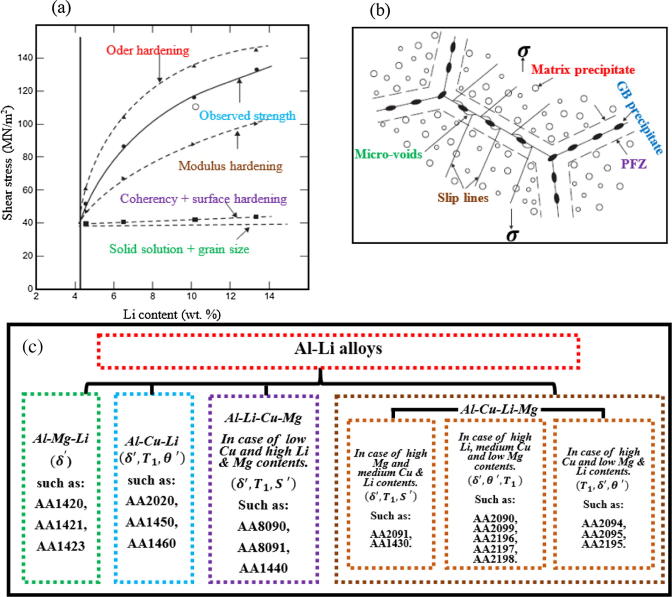
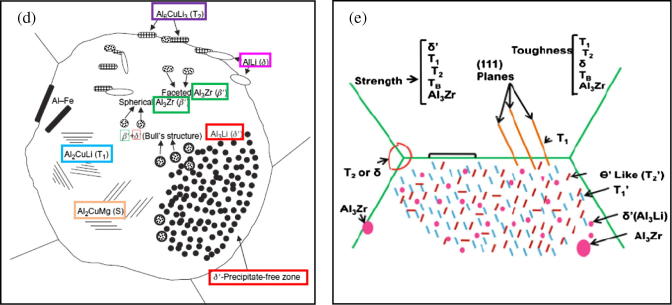
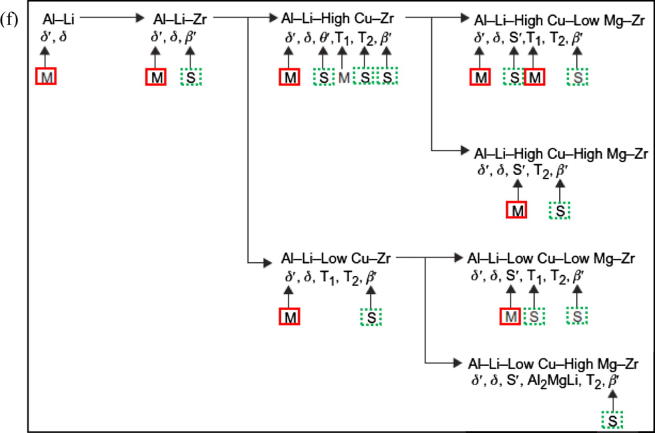
Fig. 5.
Schematic representation of (a) contribution of different strengthening mechanisms by Al3Li [66]; (b) void nucleation at GB particles when PEZs are exist [66]; (c) strengthening phases in (Al-Li-Cu) and (Al-Li-Cu-Mg) alloys; (d) a simplified explanation of precipitates microstructural in 2nd, and (e) 3rd generation Al-Li alloys [68]; (f) a graphical representation of structure of complex precipitates which constitute in Al-Li-X alloys [59], where: δ′ = (Al3Li); δ = (AlLi) equilibrium phase; θ′ = (Al2Cu); β′ = (Al3Zr); T1 = (Al2CuLi) equilibrium phase; T2 = (Al6CuLi3) equilibrium phase; S′ = (Al2CuMg), M = Major relative volume fraction and S = Minor relative volume fraction. The phases mentioned are found in different conditions of heat treatment.