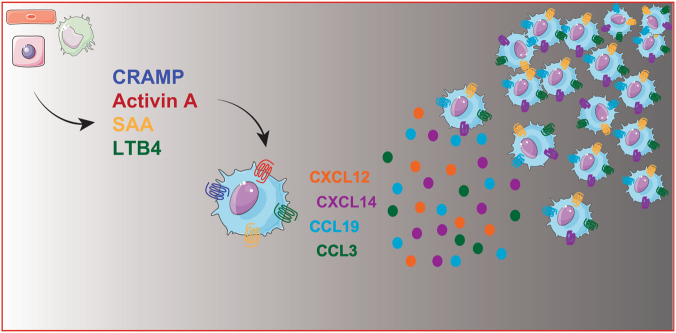
Fig. 1.
Chemokines as relay signals in the migration of DCs. This cartoon depicts the different types of chemotactic signals such as DAMPs (e.g., CRAMP; cathelin-related antimicrobial peptide), acute-phase proteins (e.g., SAA; serum amyloid A), proinflammatory cytokines (e.g., activin-A), or eicosanoids (e.g., LTB4; leukotriene B4), produced by different cell types (macrophages, endothelial cells, and hepatocytes), that, in addition to directly promoting DC migration, activate migrating cells to produce chemokines that will promote a second wave of cell recruitment