Figure 10.
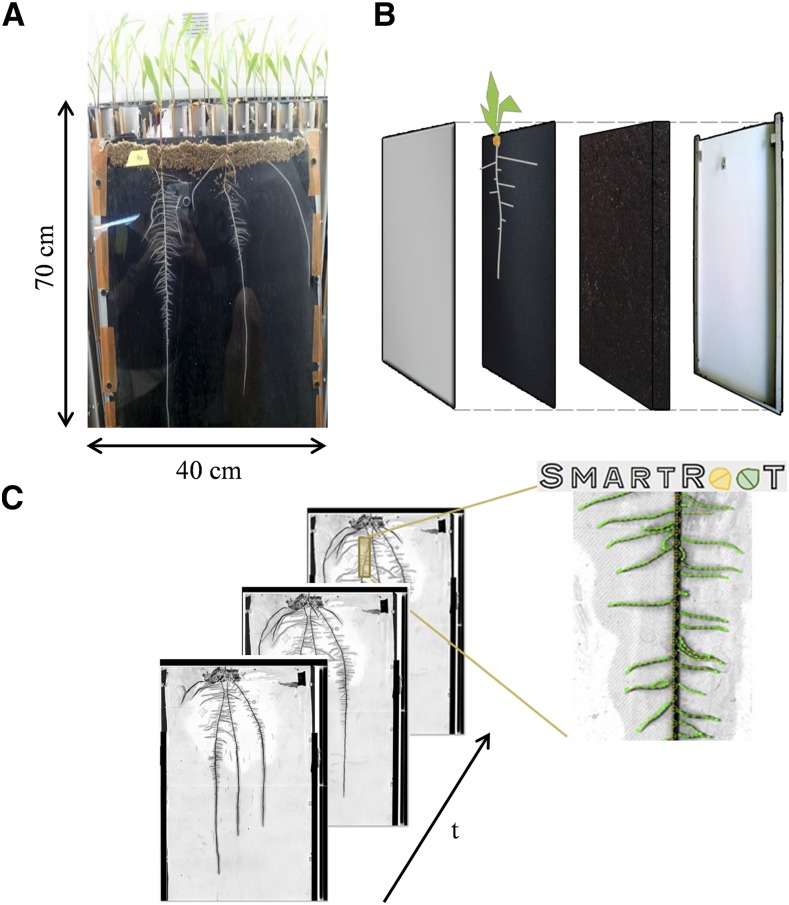
Rhizotron development and root system measurement. Root observation boxes (rhizotrons) were built according to Neufeld et al. (1989). A and B, Rhizotrons were made of (back to front) an extruded polystyrene plate, a layer of substrate (sieved peat and compost), a layer of viscose (impermeable to roots but permeable to water and nutrients), and a plexiglass plate, all joined together using aluminum U frames held by screws. Germinated seedlings with similar primary root lengths were transferred individually. A layer of wet sphagnum on the top of the rhizotrons maintained the seedlings and prevented them from drying. Rhizotrons were placed in a growth room with climatic conditions adapted to each species. Rhizotrons were scanned daily with an A3 scanner. C, The SmartRoot software (Lobet et al., 2011) was used to extract root system architecture at successive dates and to compute root growth parameters.