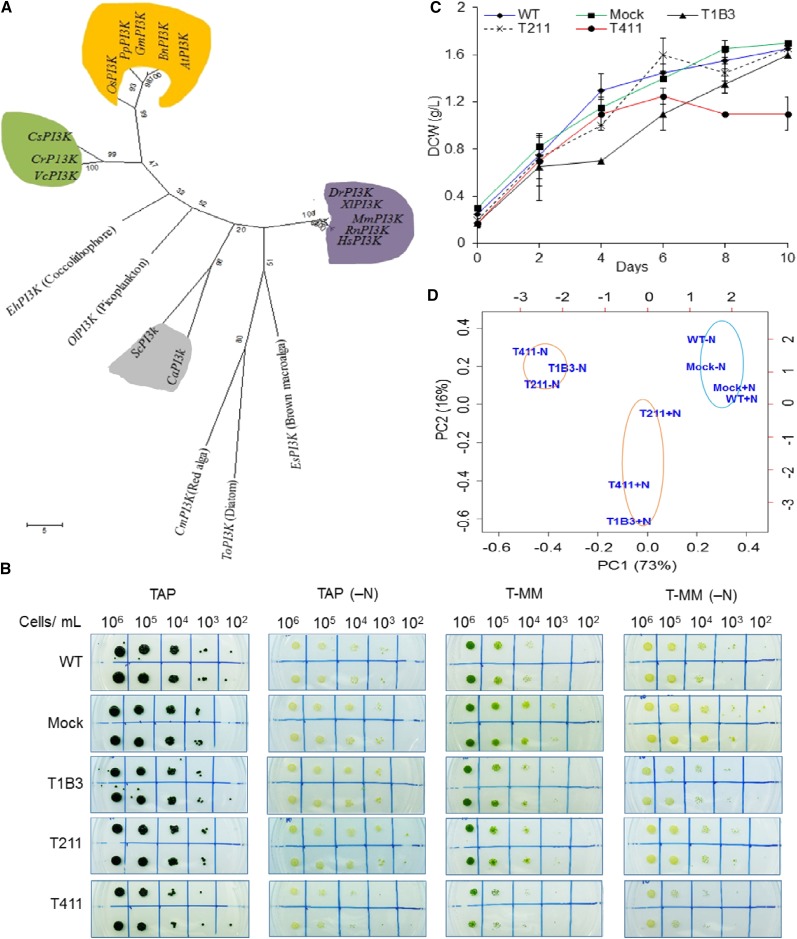
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic analysis of class III PI3K enzymes from algae, plant, and animal kingdoms and screening of VPS34 knockdown mutants through physiological analyses. A, Phylogenetic tree of class III PI3K using amino acid sequences from algae, plant, and animal kingdoms. The tree was constructed using a maximum parsimony method, and the bootstrap values (1,000 replicates) are shown on each node. Heterodimeric class III PI3K (vacuolar protein sorting 34, VPS34) of C. reinhardtii was clustered with other green algal homologs (green). PI3Ks from plants are clustered together (orange) and are closely related to green algae. The animal PI3Ks are clustered together (purple), fungi, yeast (gray), and other algal PI3Ks are not related to plant and animal PI3Ks and may have different origins. B, C. reinhardtii cc124 (wild type [WT]), the mock and the KD lines were grown in photoautrophic and mixotrophic conditions in the presence and absence of N. C, The growth pattern of wild type, mock, and mutant lines. D, Principal component analyses (PCAs) of various morphological, physiological, and genetic analyses such as area and shape, total lipid content, TAG levels, and VPS34 gene expression levels of the KD lines, mock, and wild type in both +N and −N conditions. The data used for PCA have been depicted in Supplemental Figure S2.