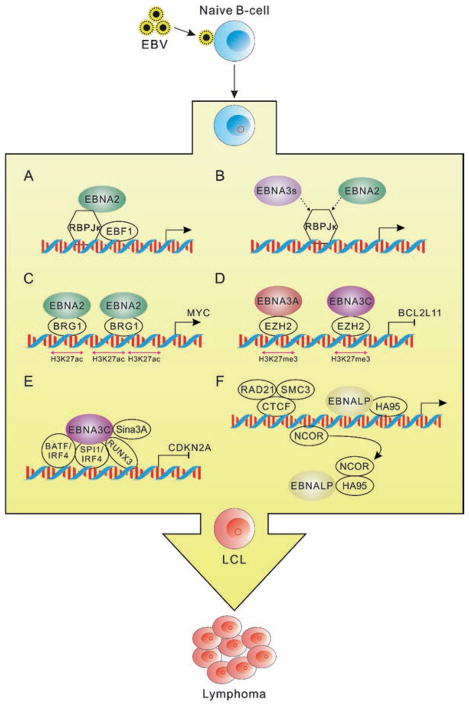
Fig. 5.1.
EBV latent antigen-associated cellular signaling pathways from the current high-throughput sequencing data during EBV-mediated lymphomagenesis. (a) EBNA2 regulates target genes expression through the recruitment of transcription factors RBPJκ and EBF1. (b) EBNA3s and EBNA2 bind with partially the same RBPJκ genomic sites. The interaction between RBPJκ and EBNA3s or EBNA2 will result in different effects of downstream gene expression, which are also associated with other EBNA-interacting cell transcription factors. (c) EBNA2 activates the three clusters of upstream enhancers of MYC promoter with increased H3K27Ac and BRG1 binding, and then EBNA2 mediates MYC activation through promoting the interaction of MYC promoter and the activated upstream enhancers. (d) EBNA3A and EBNA3C repress BCL2L11 expression by inactivating the upstream enhancers of its promoter. The inactivation is associated with increased H3K27me3 and EZH2 binding as well as the inhibition of interactions between BCL2L11 promoter and its enhancers. (e) EBNA3C binds to the promoters through BATF/IRF4, SPI1/IRF4, and RUNX and further recruits Sin3A to inhibit CDKN2A expression. (f) EBNA-LP regulates the derepression of target genes by removing NCOR repression complex from the promoters with the help of HA95 and further promotes the long-distance enhancer-promoter interaction through CTCF, RAD21, and SMC3 proteins. EBV latent antigens are highlighted by colorful patterns, while cellular factors are labeled with colorless patterns