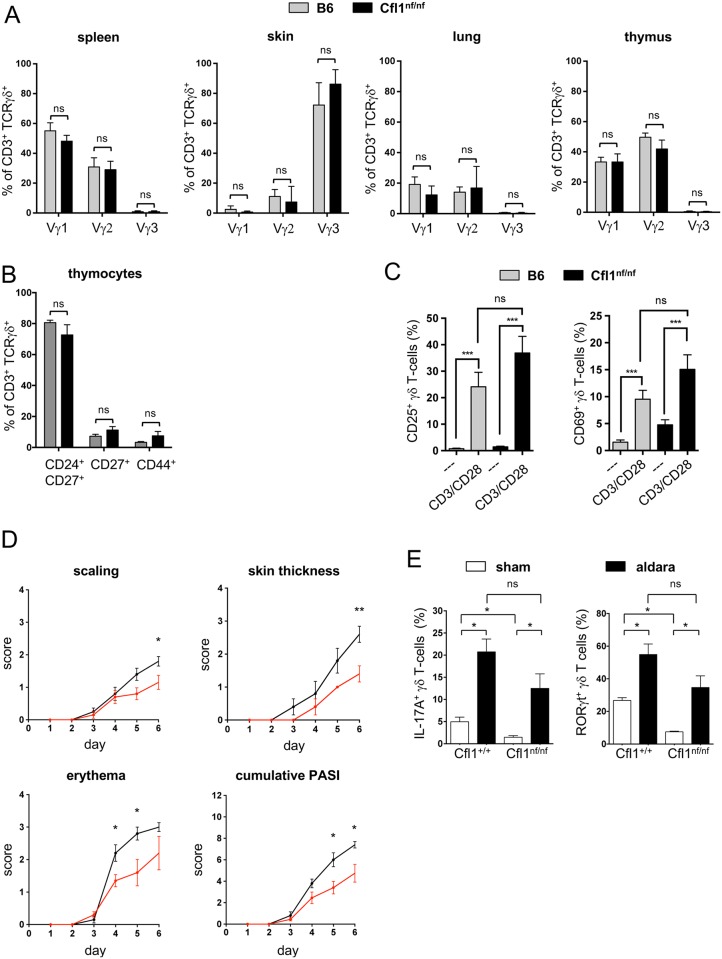
Fig 4. Cfl1nf/nf mice show normal γδ T-cell subsets which remain functional.
(A) Analysis of the surface expression of Vγ1, Vγ2, and Vγ3 of γδ T-cells isolated from the spleen, skin, lung, and thymus of B6 (grey bar) or Cfl1nf/nf mice (black bar) (n = 4 independent experiments with ≥4 mice per group). (B) Analysis of the surface expression of CD24, CD27, and CD44 of γδ thymocytes of B6 (grey bar) or Cfl1nf/nf mice (black bar) (n = 4 independent experiments with ≥4 mice per group). (C) In vitro activation of splenic γδ T cells of Cfl1nf/nf (black bar) and control mice (grey bar) by plate-bound CD3 and CD28 antibodies for 24 h. Determination of the T-cell activation markers CD25 (left bar chart) and CD69 (right bar chart) by flow cytometry. (D) Age- and sex-matched Cfl1nf/nf (red line) and Cfl1+/+ (black line) mice at 7 weeks of age were used for an IMQ-induced psoriasis-like model. Over 6 days, prior to topical application of IMQ, scores of individual parameters such as scaling, back skin thickness, and erythema formation were measured and the accumulated PASI was calculated. (E) Flow cytometric analysis of IL-17A and RORγt expression in γδ T cells of skin-draining LNs. Cytokine production was assessed after 6 days of topical application of IMQ containing Aldara crème (Sham) or control crème (Aldara) (experiment with ≥4 mice per group). Data are represented as mean ± SEM. **** p < 0.0001; *** p < 0.001; ** p < 0.01; * p < 0.05; Underlying data can be found in S1 Data. Cfl1, cofilin-1; IMQ, imiquimod; ns, not significant; PASI, psoriasis area severity index.