Figure 4.
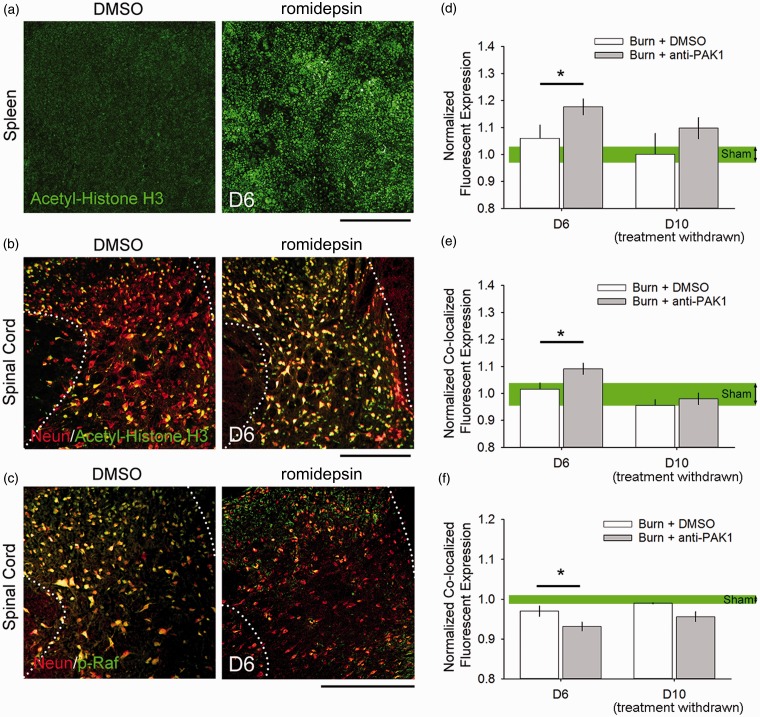
Romidepsin has bioavailability and tissue action in the spinal cord. To assess the bioavailability of romidepsin through our study, we measured the expression of biomarkers for drug-tissue response in the spleen and spinal cord at Day 6 (<24 h after treatment) and Day 10 (after drug withdrawal). At Day 6, we observed an increase in histone acetylation in the (a, d) spleen and (b, e) neurons in the spinal cord dorsal horn (co-localized immunoreactivity of acetyl-histone H3 with NeuN), as compared with DMSO treatment (*p < 0.05). At Day 10, there was no difference in histone acetylation between burn-injured treatment groups (p > 0.05). Additionally, on Day 6, we observed (c, f) a decrease in Pak1 effector, p-RAF, expression in neurons in the spinal cord dorsal horn (*p < 0.05). There was no difference in p-RAF expression on Day 10 following drug withdrawal (p > 0.05). In comparisons with Sham, we observed no difference in biomarker expression levels in burn-injured animals at any time point (p > 0.05). Scale bars in (a) to (c) are 500 µm. Graphs are mean ± SEM. DMSO: dimethyl sulfoxide.