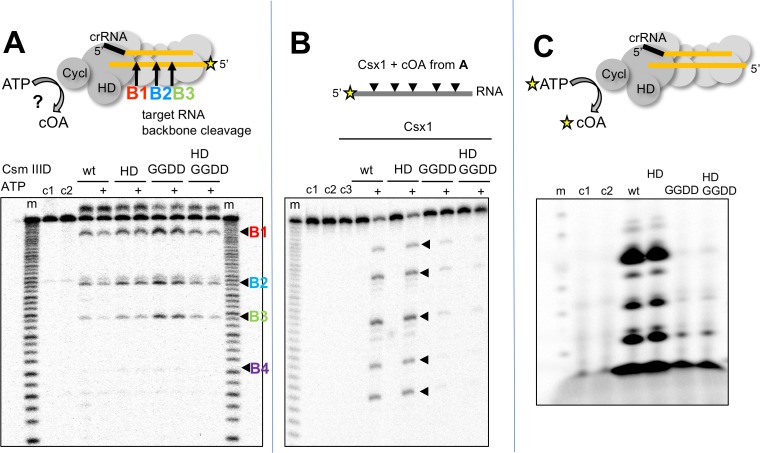
Figure 2. S. solfataricus Csm synthesises cOA on target RNA binding, activating the Csx1 nuclease.
(A) Backbone-mediated cleavage of a labelled target RNA. Three prominent cleavage sites (B1–B3) are indicated. Abrogation of the HD nuclease (HD) or cyclase (GGDD) domain active sites has no effect on this activity. The marker lanes (m) are generated by alkaline hydrolysis of the target RNA. The presence of ATP in the reaction is indicated by a ‘+’ symbol. Control lanes c1 and c2 represent incubation without Csm complex in the presence and absence of ATP, respectively. The diffuse density above the intact RNA is an artefact of electrophoresis. The yellow stars indicate the presence of a radioactive label. (B) Activation of the CARF nuclease Csx1 (Sso1389) by the reaction products of the Csm reaction in A. Csx1 is inactive against the labelled substrate RNA unless activated by the products of the Csm reaction. This activation is dependent on the presence of ATP in the original reaction and an intact cyclase domain. Control lanes c1 and c2 represent incubation of the RNA in buffer at 4 and 50°C, respectively, whereas c3 is a control in presence of Csx1 without added supernatant from Csm reaction. (C) Analysis of the products generated by Csm on addition of target RNA and α−32P-ATP. These products are dependent on the presence of an active cyclase domain. They represent a range of linear and cyclic polyadenosines of varying sizes. Control lanes c1 and c2 respectively represent the reaction in absence of Csm or in presence of Csm without target RNA.