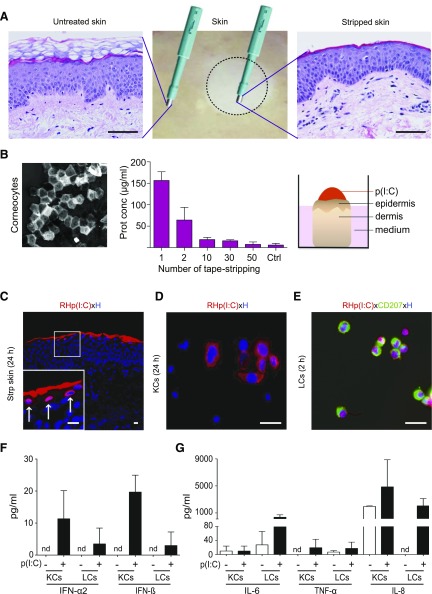
Figure 1.
Rhodamine (RH)-labeled p(I:C) is taken up by epidermal cells. A) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of paraffin-embedded sections from healthy human skin (middle) indicates efficient removal of stratum corneum in tape-stripped skin (right) compared to untreated skin (left). Scale bars, 50 µm. B) One representative strip disc with corneocytes is shown (left). Protein estimation of each strip disc was analyzed with bicinchoninic acid protein assay. Data are represented as means ± sem of measurements obtained with 4 different donors (middle). Schematic representation of p(I:C) application (right). C) Immunofluorescence staining of cryostat section from stripped cultured skin showing uptake of RH-labeled low MW p(I:C) (red) in epidermal cells. Shown is single representative of 3 biopsy samples from different donors. Scale bars, 10 µm. Arrows in inset show RH+ KCs. D, E) Representative images of primary KCs (60% confluency) and sorted CD207+ LCs (300 cells/slot) showing uptake of RH-labeled p(I:C) at 24 and 2 h, respectively. Data are from 1 of 3 similar experiments from different donors. Nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst (blue). Scale bars, 20 µm. F, G) Freshly isolated and sorted KCs and LCs from same donor were cultured for 48 h with unlabeled, low MW p(I:C) (+) or left untreated (−). Indicated cytokine concentrations from supernatants were determined with LegendPlex Bead Array. Results are expressed as means ± sem of duplicate cultures from 1 experiment, representative of 2 with different donors.