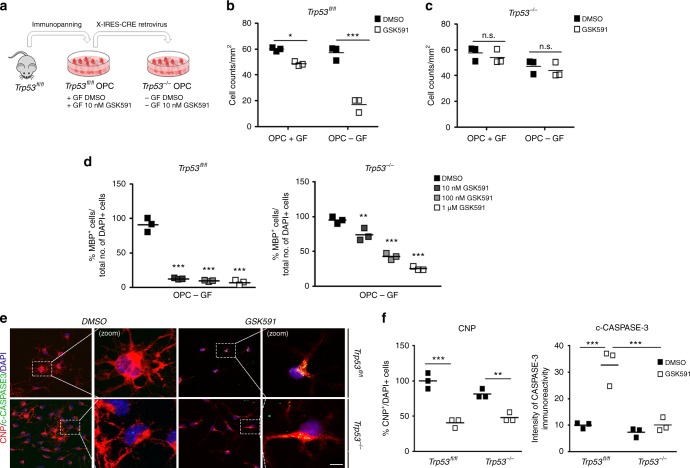
Fig. 5.
Activation of p53-dependent apoptosis in progenitors treated with PRMT5 inhibitors. Effect of the pharmacological inhibitor of PRMT5 (GSK591) on cell viability and differentiation of primary cultures of OPCs from wild-type (Trp53fl/fl) and p53 mutant (Trp53−/−) mice. a Schematics of experimental conditions. b Average cell counts from three biological replicates of wild-type (Trp53fl/fl) and (c) Trp53-null (Trp53−/−) OPC cultures in the presence (+GF) and absence (−GF) of growth factors, and with or without 10 nM GSK591. d Average MBP+ cell counts from three biological replicates of wild-type (Trp53 fl/fl) and p53 mutant (Trp53−/−) OPCs cultured in differentiating conditions in the absence (DMSO) or presence of increasing concentration of GSK591. One-way ANOVA, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001. e Representative confocal images of wild-type (Trp53fl/fl) and Trp53-null (Trp53−/−) OPCs cultured in differentiating conditions, with or without 10 nM GSK591 and stained with antibodies specific for CNP (red), cleaved CASPASE-3 (c-CASPASE3, green), and DAPI (blue) (scale bar = 10 μm). f Scatter plots of the average number of CNP+ cell relative to total DAPI+ cells and average intensity of cleaved CASPASE-3 staining from three biological replicates of GSK591-treated wild-type (228 total cells counted) and Trp53-null OPCs (232 total cell counted) relative to untreated wild-type (240 total cells counted) and Trp53-null (256 total cell counted). One-way ANOVA, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. n.s. nonsignificant