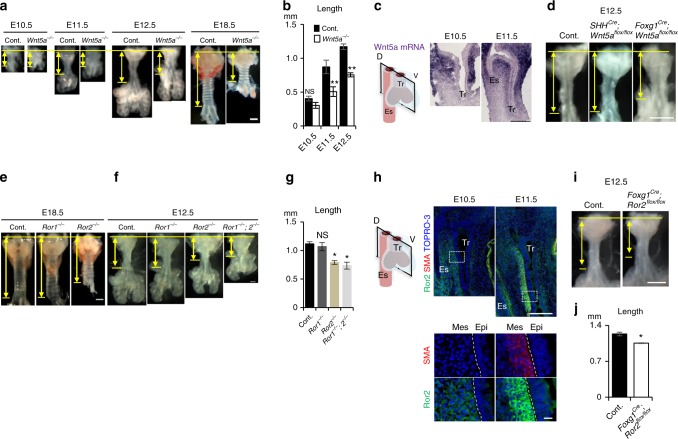
Fig. 3.
Wnt5a-Ror2 signaling is involved in tube elongation. a Gross morphology of a developing Wnt5a−/− trachea and littermate control. b Tracheal tube length (control; n = 4–6, Wnt5a−/−; n = 3). c In situ hybridization for Wnt5a mRNA in developing tracheas. d Gross morphology of Foxg1Cre; Wnt5aflox/flox trachea (n = 4), SHHCre; Wnt5aflox/flox (n = 3) trachea, and littermate control (n = 7) at E12.5. Gross morphology of Ror1 and/or 2−/− trachea and littermate control at E18.5 (e) and 12.5 (f). g Tracheal tube length (control; n = 4, Ror1−/− = 5, Ror2−/− = 5, Ror1−/−; Ror2−/− = 3). h Ror2 and SMA expression in developing tracheas. Sections were stained for Ror2 (green), SMA (red), and TOPRO-3 (blue). Lower panels show higher magnification images of dotted squares. Dotted lines indicate epithelium–mesenchyme boundary. i Gross morphology of Foxg1Cre; Ror2flox/flox trachea and littermate control at E12.5. j Tracheal tube length (control; n = 5, Foxg1Cre, Ror2flox/flox; n = 9). Yellow arrows indicate trachea length. D dorsal; V ventral; Epi epithelium; Mes mesenchyme; Tr trachea; Es esophagus. P values (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01) show the significance with Student’s t test (b) or the Tukey-Kramer method (g). Scale bar = 500 μm (a, d, e, i), 200 μm (c, e, h; upper panel), 10 μm (h; lower panel)