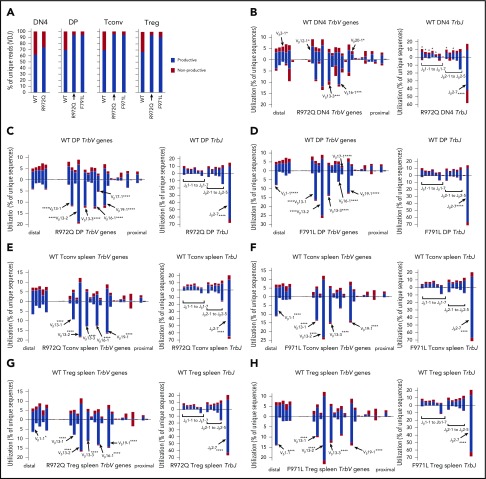
Figure 7.
Abnormalities of Trb repertoire in Rag1-mutant mice. (A) Percentage of productive and nonproductive reads of total unique Trb joins from WT and R972Q DN4 thymocytes (CD4−CD8−CD44−CD25−); WT, R972Q, and F971L CD4+CD8+ DP thymocytes; WT, R972Q, and F971L Tconv (CD4+EGFP−) cells; and WT, R972Q, and F971L Treg (CD4+EGFP+) cells. (B) Utilization of V (left) and J (right) genes in Trb rearrangements in DN4 thymocytes (CD4−CD8−CD44−CD25−). Top shows WT mice; bottom shows R972Q mice. (C) Trb unique sequences in CD4+CD8+ DP thymocytes. Top shows WT mice; bottom shows R972Q mice. (D) Trb unique sequences in CD4+CD8+ DP thymocytes. Top shows WT mice; bottom shows F971L mice. (E) Trb unique sequences in splenic Tconv (CD4+EGFP−) cells from WT (top) and R972Q (bottom) mice. (F) Trb unique sequences in splenic Tconv (CD4+EGFP−) cells from WT (top) and F971L (bottom) mice. (G) Utilization of V (left) and J (right) genes in Trb unique sequences in splenic Treg (CD4+EGFP+) cells from WT (top) and R972Q (bottom) mice. (H) Utilization of V (left) and J (right) genes in Trb unique sequences in splenic Treg (CD4+EGFP+) cells from WT (top) and F971L (bottom) mice. χ2 test: *P ≤ .05, ***P ≤ .001, ****P ≤ .0001.