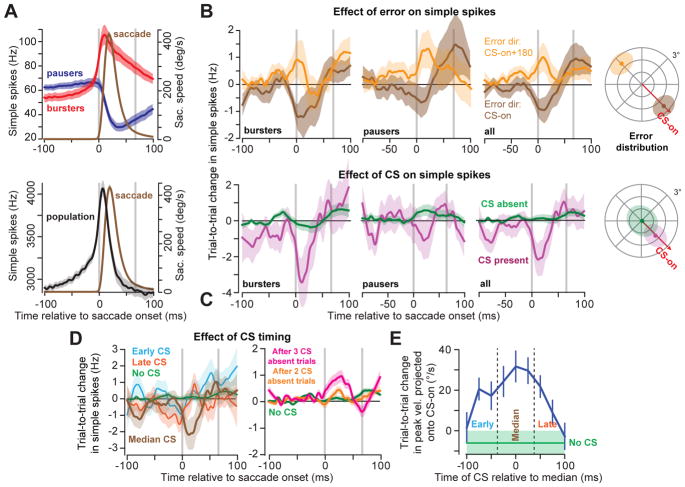
Figure 3. Complex spikes cause trial-to-trial depression in simple spike responses.
A. Average activity for all bursting (red) and pausing (blue) cells (top). Vertical gray lines indicate saccade onset and end. While neither of these subpopulations predict eye speed in real-time, their combined activity (bottom) into a population predicts the real-time speed of the eye4. B. Effect of error on simple spikes. Following an error in CS-on (high probability of CS), both burst and pause cells reduced their activity (top) whereas when the probability of CS was low (CS-on+180°), these cells increased their activity. The mean response across P-cells showed trial-to-trial changes which paralleled the responses of burst and pause cells. C. Effect of CS on simple spikes. When a CS was present within 25ms of the median CS response time in the post-saccadic period, simple spikes changed in the next trial for bursters, pausers, and across all cells (magenta), whereas when a CS was absent (green), there was little/no change in simple spike response on the next trial. D. CS timing played a critical role in changing the simple spikes. If the CS occurred during a temporal window of 50ms centered on the median CS time, it produced larger trial-to-trial change in simple spikes (brown) than if the CS occurred earlier (cyan) or later (red) than this time period. Lack of a CS (green) in a single trial was followed by little or no change in the simple spikes. Persistent lack of a CS in two (green) or three (red) trials resulted in increased simple spikes. E. A CS that occurred around the median period was most effective in producing trial-to-trial change in behavior. In all cases, median timing refers to a within-cell measure of post-saccadic distribution of CS timing. All error bars are standard error of the mean (SEM)across n=67 P-cells, except for part (A), where it reflects 95% confidence interval about the mean of bootstrap population of 50 randomly selected P-cells. Simple spike data were smoothed with a Savitzky-Golay filter with a width of 25ms.