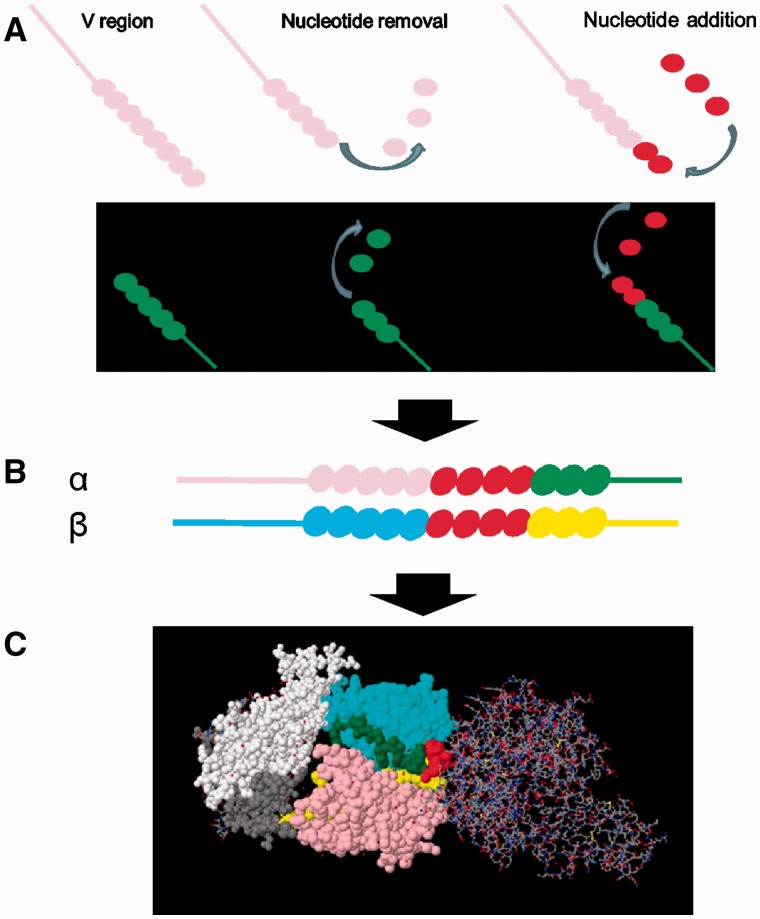
Figure 1.
T-cell recombination and the generation of diversity. Individual V and J genes are selected stochastically (but not uniformly) and recombined during T-cell development in the thymus. During recombination base pairs can be removed and/or added at the junction before the final ligation (A). Both alpha and beta genes undergo recombination independently. Beta genes incorporate an additional D region minigene between V and J, giving rise to two junctions (not shown). Finally, alpha and beta V regions are transcribed, spliced onto their respective constant regions (B) and translated, and the two proteins heterodimerize to give rise to a single TCR (C). The TCR/MHC/peptide complex shown here is derived from the PDB structure 1FYT, and displayed using RasMol [3]. The TCR is shown in space fill, and the peptide/MHC complex is shown in stick representation on the right. Pink – Vα; yellow – Jα; blue – Vβ; green – Jβ; and red – CDR3.