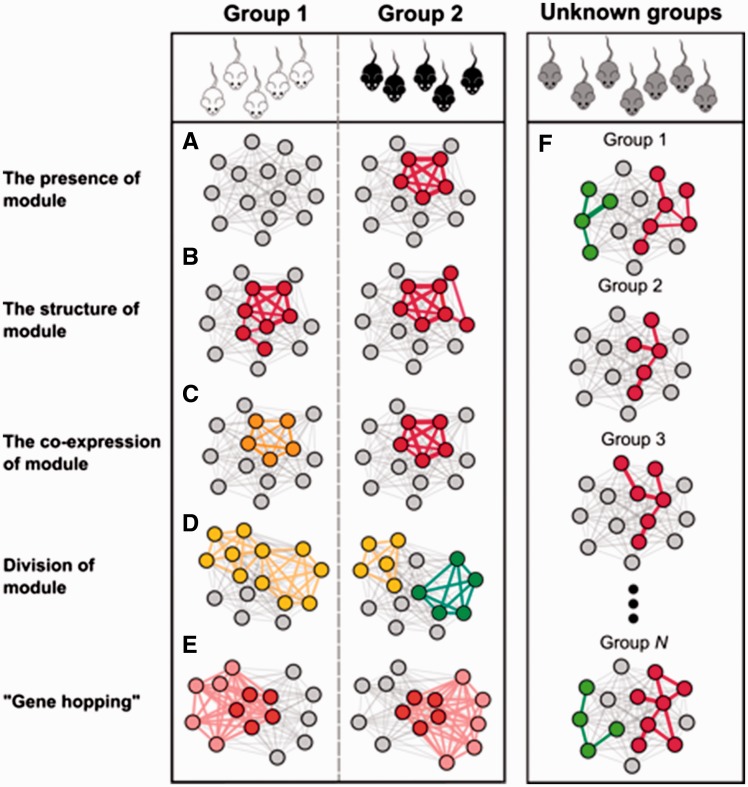
Figure 3.
Changes in gene co-expression patterns that can occur between samples. Differential co-expression can occur as the presence of a module in only one of the sample groups (A), as differences in the structure of the module (B) or as differences in the correlation strength between members of the modules (C). Additionally, differential co-expression can be detected if one larger interconnected module splits into several smaller ones (D) or if a group of genes changes its correlation partners [‘gene hopping’ (E)]. If sample groups are not defined before the differential co-expression analysis, or are unknown, biclustering methods can identify modules unique to a subpopulation of samples by simultaneously classifying the samples into groups in which these modules exist (F).