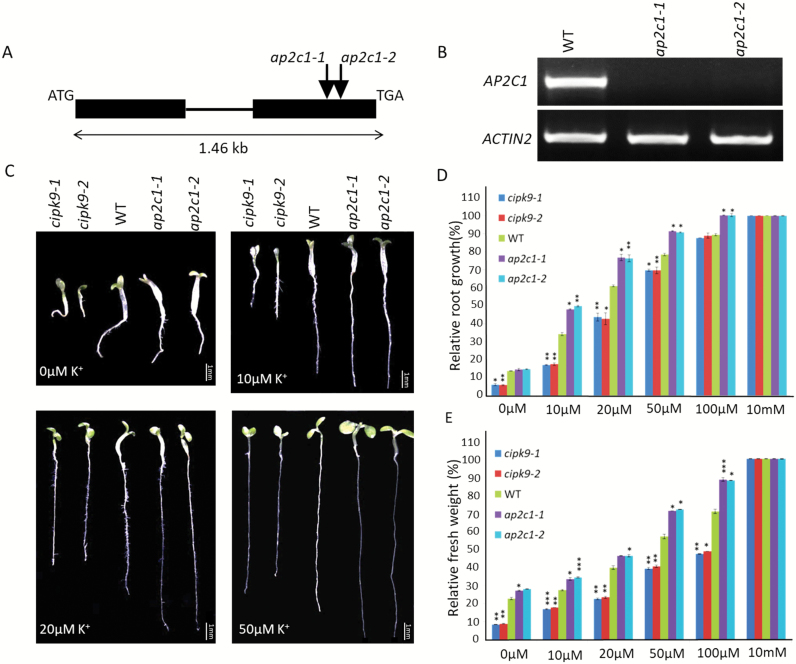
Fig. 5.
Phenotypes of seedlings of AP2C1 and CIPK9 null mutants on K+-deficient media. (A) Schematic of the AP2C1 gene structure. Exons (closed boxes) and introns (lines) are indicated. The positions of the T-DNA insertions are indicated by arrows. (B) RT-PCR analysis using AP2C1 gene-specific primers confirmed the null mutant alleles of AP2C1 (ap2c1-1, ap2c1-2). Expression of ACTIN2 was used as an endogenous control. (C) Growth of cipk9-1, cipk9-2, wild-type (WT, Col-0), ap2c1-1, and ap2c1-2 under different K+ concentrations (as indicated) after 7 d. The 10 mM K+ concentration was used as the control (similar to half-strength MS medium). Scale bars are 1 mm. (D) Quantitative assessment of AP2C1 and CIPK9 null mutant phenotypes under different K+ conditions after 7 d. The data show root growth relative to that of the WT at 10 mM K+.(E) Fresh weight of 7-d-old seedlings grown with different K+ concentrations. The data show fresh weight relative to that of the WT at 10 mM K+. In (D, E) 20 seedlings of each genotype were used for analysis and three independent experiments were conducted (n=3); data are means (±SD). *P<0.05, ** P<0.01, ***P<0.005.