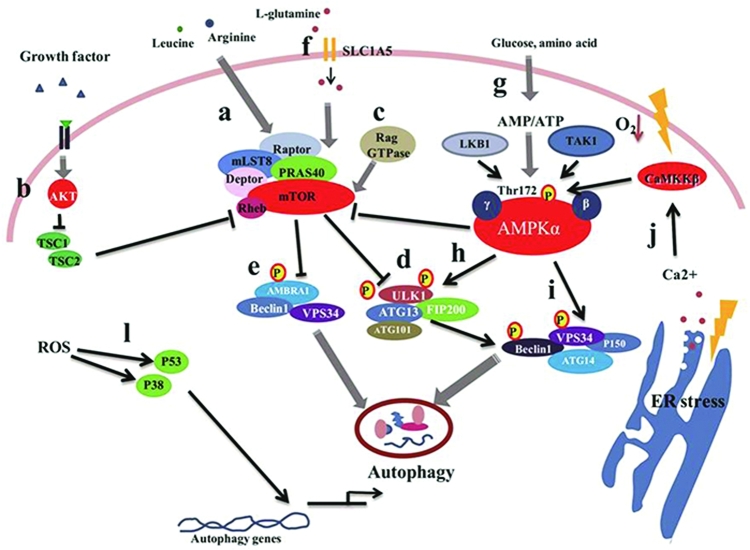
FIGURE 2.
Autophagy induced by nutrient and nutrition stresses via the mTOR and AMPK signal pathways. In response to nutrient deficiency or stress conditions, mTOR is activated following the suppression of the autophagy pathway, whereas energy withdrawal stimulates AMPK activation. This then inhibits mTOR activity by phosphorylation, which promotes the induction of autophagy. ER stresses, hypoxia, and ROS can induce autophagy by enhancing autophagy gene transcription or stimulating the AMPK pathway. (a) The highly conserved Ser/Thr protein kinase TOR is a key sensor and integrator of the amino acid pool signaling. mTORC1 comprises mTOR, Raptor, mLST8, PRAS40, and Deptor. (b) The growth factors regulate mTORC1 through the AKT-TSC1/TSC2 pathway. When growth factors exist, AKT is activated to inhibit TSC1/TSC2 to activate mTORC1, which inhibits the autophagy pathway. (c) The Rag GTPases can activate mTORC1 in response to amino acid signaling by directly binding and activating mTORC1. (d) ATG13 and ULK1, which form complexes with FIP200, can be directly phosphorylated by mTOR to inhibit ULK1 complex activity. (e) AMBRA1, with its ULK1-dependent pattern, induces autophagosome nucleation by promoting Beclin 1 interaction with VPS34. (f) The flux of L-glutamine has been found to be controlled by 2 transporters: SLC1A5 and SLC7A5/SLC3A2. (g) Environmental AMP, ADP, or ATP can directly bind AMPK via the adenine nucleotide-binding sites of the γ subunit. (h) Under glucose deficiency, activation of AMPK promotes autophagy induction by increased ULK1 autophosphorylation. (i) Upon glucose deficiency, the activity of different VPS34 complexes, which include VPS34, p150, ATG14, and Beclin 1 or UVRAG, is regulated. (j) The ER is the site of cellular Ca2+ storage, and continuous removal of Ca2+ from the ER lumen to the cytosol can induce ER stress. An increase in cytosolic Ca2+ has been shown to lead to initiation of autophagy. The ROS-mediated autophagy induction is P53 and P38 dependent. When ROS accumulate, P53 and P38 pathways activate to upregulate autophagic gene expression, which initiates autophagy. AMBRA1, autophagy and beclin regulator 1; AMPK, AMP-activated kinase; ATG, autophagy-related gene; CaMMKβ, calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase beta; Deptor, DEP-domain-containing mTOR-interacting protein; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; FIP200, FAK-family interacting protein of 200 kDa; LKB1, liver kinase B-1; mLST8, mammalian lethal with Sec13 protein 8; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; PRAS40, proline-rich AKT substrate 40 kDa; Raptor, regulatory-associated protein of mTOR; Rheb, Ras homolog enriched in brain; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SLC1A5, solute carrier family 1 member 5; TAK1, transforming growth factor beta-activated kinase 1; TSC, tuberous sclerosis complex; ULK1, Unc-51 like autophagy activating kinase 1; UVRAG, UV radiation resistance associated gene; VPS34, vacuolar protein sorting 34.