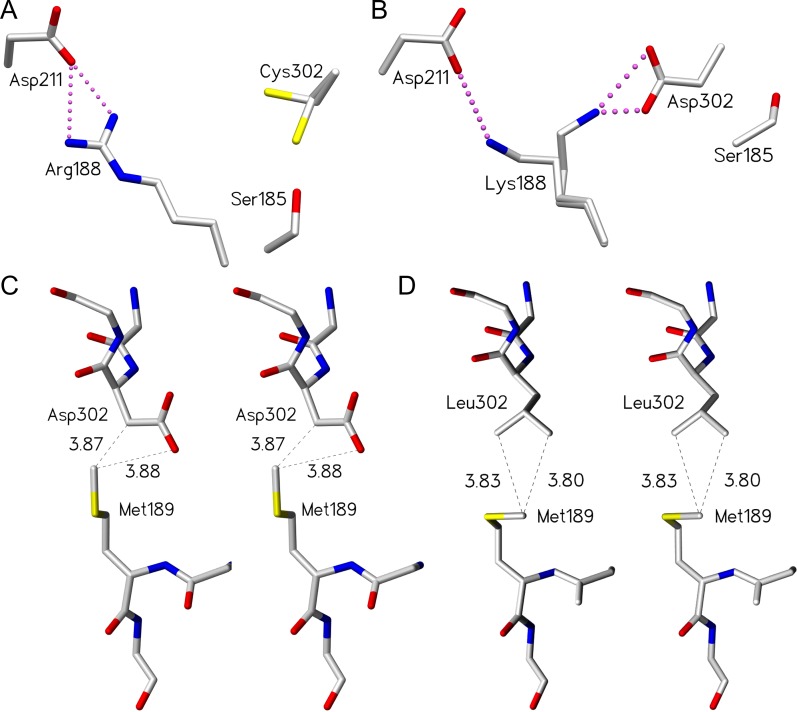
Fig. 5.
Certain mutants of residue 302 and 188 are able to compensate for the loss of critical hydrogen bonds within the salt bridge network by establishing alternative interactions. D302C and R188K mutants maintain the salt bridge network by adopting multiple conformations, while the D302L mutant maintains partial loop order via van der Waal’s contacts. (A) Cys302 side chain observed in two conformations in unliganded GTA/D302C. (B) Lys188 side chain observed in two conformations in unliganded GTB/R188K. Stereoview of (C) wild-type GTB residues Asp302 and Met189 (PDB code 2RIT) and (D) GTB/D302L residues Leu302 and Met189 with van der Waal’s interactions shown as dashed lines (distances shown in Ångstrom) between the leucine side chain carbon atoms and the methionine side chain methyl group. The dashed lines between the Met189 methyl group and the Asp302 carbonyl group represent a measured distance, not a van der Waal’s interaction. Atoms are colored by element with carbon gray, oxygen red, nitrogen blue and sulfur yellow. Salt bridge interactions are depicted as pink dashed spheres.