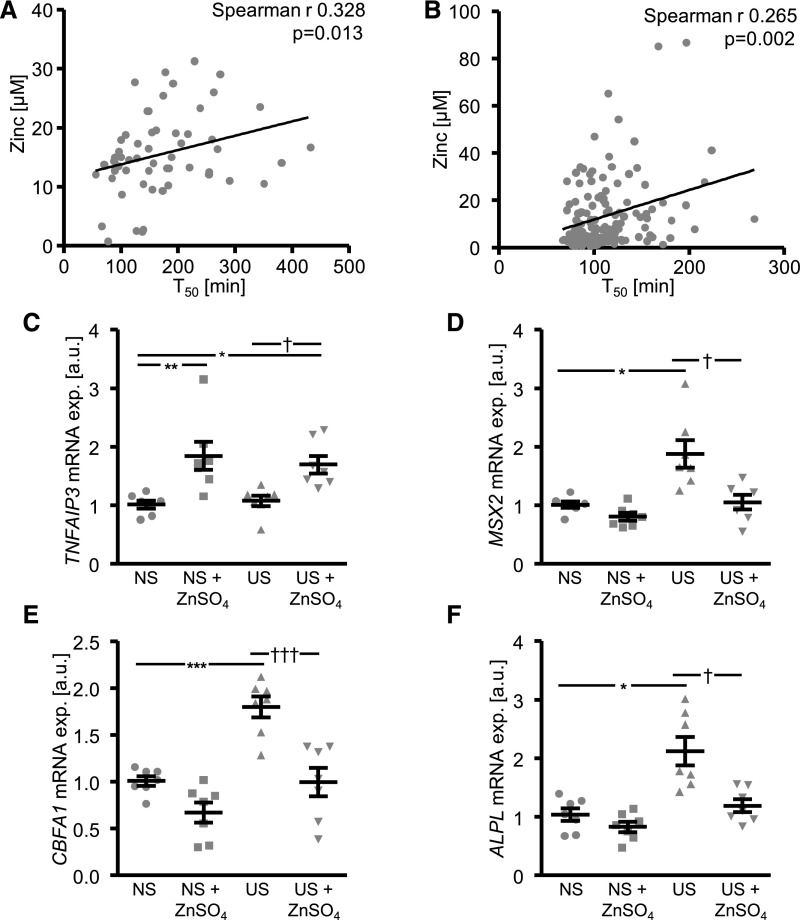
Figure 8.
Serum zinc levels associate with serum calcification propensity in patients with CKD and ZnSO4 supplementation inhibits uremic serum-induced osteoinductive signaling in HAoSMCs. (A) Scatterdot plot of correlation between serum zinc concentrations (micromolar) and serum calcification propensity measured as calciprotein particle maturation time (T50, minute) in human healthy volunteers and patients with CKD (n=57). (B) Scatterdot plot of correlation between serum zinc concentrations (millimolar) and serum calcification propensity measured as calciprotein particle maturation time (T50, minute) in a second cohort of human patients with CKD (n=138). P values are indicated in the figure. (C–F) Scatterdot plots and arithmetic means±SEM (n=7; arbitrary units, a.u.) of TNFAIP3 (C), MSX2 (D), CBFA1 (E), and ALPL (F) relative mRNA expression in HAoSMCs after treatment with normal or uremic serum without or with additional treatment with 15 µM ZnSO4. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001 statistically significant versus normal serum treated HAoSMCs; †P<0.05; †††P<0.001 statistically significant versus uremic serum treated HAoSMCs. NS, normal serum; US, uremic serum.