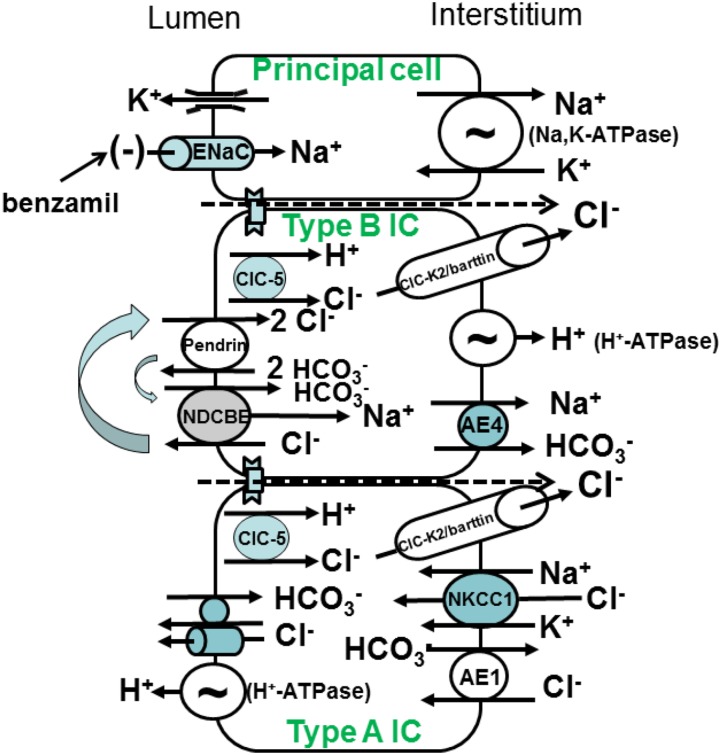
Figure 1.
Ion transporters in mouse cortical collecting duct. Mouse cortical collecting duct is made up of principal cells, which mediate electrogenic Na+ absorption through the benzamil-sensitive epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC) on the apical plasma membrane. Na+ exits principal cells across the basolateral plasma membrane through the Na,K-ATPase. ENaC-mediated Na+ absorption creates a lumen-negative voltage, which provides the driving force for K+ secretion. Type B ICs mediate electroneutral NaCl absorption and HCO3− secretion through an apical plasma membrane Na+-independent electroneutral Cl−/HCO3− exchanger (pendrin) that acts in tandem with an Na+-dependent Cl−/HCO3− exchanger. NaCl exits the cell through a basolateral plasma membrane Cl− channel and an NaHCO3 cotransporter (AE4). Net H+ equivalents exit across the basolateral plasma membrane through the H+-ATPase. The type A IC mediates uptake of H+ equivalents and Cl− across the basolateral plasma membrane through Na+-K+-2Cl− cotransporter 1 (NKCC1), Cl−/HCO3− exchange (AE1), and possibly, a Cl− channel. This cell type secretes HCl through an apical H+-ATPase and an apical Cl− channel or Cl−/HCO3− exchanger.