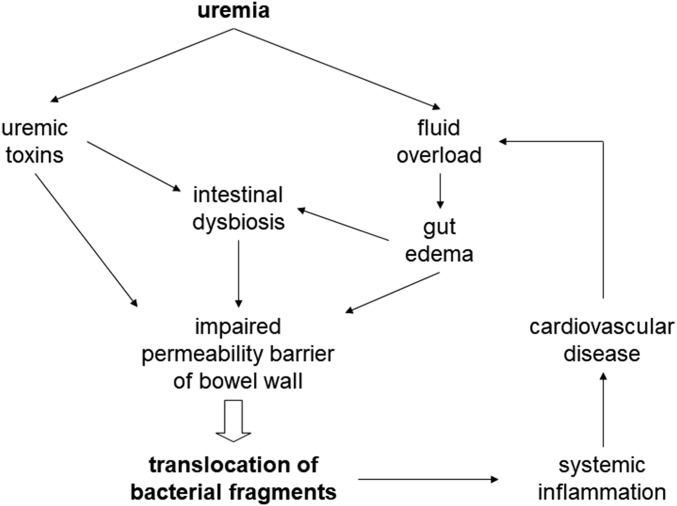
Figure 1.
Pathogenic mechanism and consequence of bacterial fragment translocation in uremia. Organic uremic toxins may affect intestinal barrier function directly or via the proliferation of dysbiotic bacteria in the gut. In addition, renal failure results in fluid overload and gut edema, which also affects the intestinal barrier function. The end result is translocation of bacterial fragments to the systemic circulation, which leads to systemic inflammation and cardiovascular disease, resulting in a vicious cycle by further aggravating fluid overload.