Figure 1.
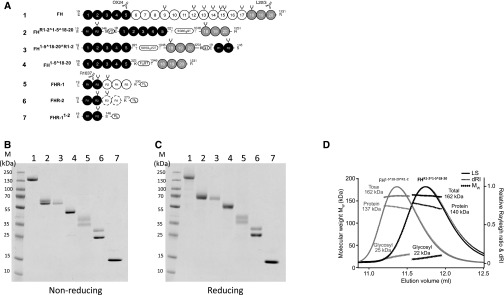
New mini-FH molecules dimerize in solution. (A) The FH family of proteins and derived recombinant proteins comprise SCR domains, which are represented by gray-scaled ovals to indicate the natural source of the module and their biochemical function. Constructs are numbered (1–7) and correspond to the lane identifiers in the analysis shown in (B) and (C). The amino acid sequences are on the basis of the UniProt database (FH accession no. P08603; FHR-1 accession no. Q03591; FHR-2 accession no. P36980) with single letter code used in the protein segments that have been shuffled into the recombinant constructs. Artificial linker sequences are indicated by boxes and glycosylation sites are indicated by black forks. mAb epitopes are indicated; OX24 and L20/3 antibodies recognize FH SCR 5 or SCR 20, respectively, whereas R1037 (a mouse mAb produced in-house against recombinant FHR1) recognizes FHR-1 SCR 1–2. (B) A nonreducing and (C) reducing 10%–20% gradient SDS-PAGE comparison of plasma purified human FH and recombinant FH1–5^18–20, FHR1–2^1–5^18–20, FH1–5^18–20^R1–2, and all other control proteins. (D) SEC-MALS analysis of FHR1–2^1–5^18–20 (black) and FH1–5^18–20^R1–2 (gray). Molecular mass analysis (assuming unmodified proteins) reveals that FHR1–2^1–5^18–20 and FH1–5^18–20^R1–2 are dimeric species of 162 kD (approximately 22 kD sugar and approximately 140 kD protein), respectively. Light scattering (LS) and differential refractive index (dRI) are shown as solid and dashed lines, respectively, with fitted molecular masses (Mw) plotted as diamonds across elution peaks.