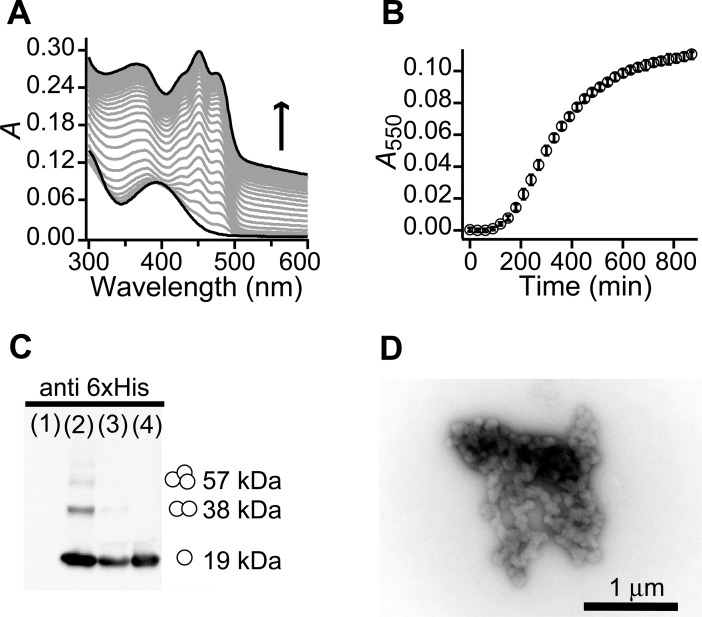
Fig 1. VVD exhibits amorphous aggregation at standard conditions.
(A) The absorbance (A) spectra of VVD (0.56 mg/mL, 31 μM) at 25°C and standard buffer conditions (10% glycerol, 50 mM HEPES, 150 mM NaCl, 20 mM imidazole, pH 8) acquired every 30 min after a BL pulse, show a shift in absorbance. First and last spectra are shown in black. Arrow indicates time course of the absorbance shift. (B) The aggregation of VVD was quantified by measuring the absorbance at λ = 550 nm. A representative VVD aggregation kinetics record (0.56 mg/mL) is shown (mean ± SD, N = 3). (C) A Western blot against VVD´s 6×His shows that samples with an absorbance shift form VVD oligomers. Control samples in lanes 1 and 4 correspond to bovine serum albumin (BSA) and unaggregated protein, respectively. The pellet and the supernatant of a centrifuged aggregated VVD sample were loaded in lane 2 and 3, respectively. The pellet fraction presents three bands at molecular weights corresponding to monomer (19 kDa), dimer (38 kDa) and trimer (57 kDa) of VVD. (D) Transmission electron microscopy of VVD samples with absorbance shifts display amorphous aggregation.