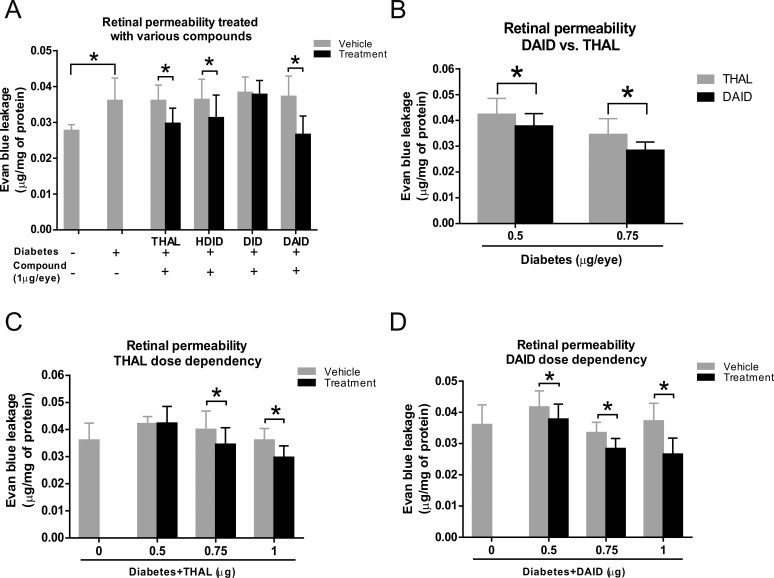
Figure 3.
Effect of thalidomide (THAL), HDID, DID, and DAID on retinal vascular leakage in STZ-induced diabetes rats. (A) Two weeks after the induction of diabetes by STZ, diabetic rats received an intravitreal injection of 1.0 μg/eye (5 μl/eye, 0.2 mg/ml in BN rat serum) of thalidomide, HDID, DID, and DAID into the right eye and an equal volume of the vehicle into the left eye. Retinal vascular permeability was measured using Evans blue dye-albumin complex leakage method, 2 days after the injection and normalized by the total protein concentration in the retina. The data showed significantly higher vascular permeability in diabetic rats at 2 weeks after STZ injection compared to nondiabetic rats. (B) DAID induced more potent reduction of retinal vascular leakage compared with thalidomide at the doses of 0.5 and 0.75 μg/eye. (C, D) STZ-induced diabetic rats received an intravitreal injection of DAID or thalidomide at doses as indicated 2 weeks after the induction of diabetes. Permeability was measured 48 hours after the injection and expressed as μg of Evans blue per mg of protein in the retina. All values are mean ± SD, n = 6, *P < 0.05 (1-way ANOVA).