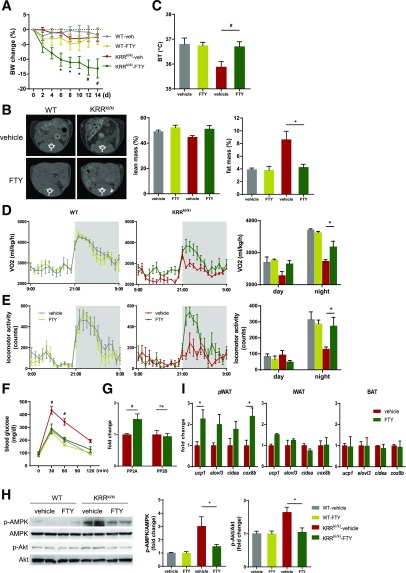
Figure 5.
Rescue of central PP2A activity improves metabolic abnormalities in KRRki/ki mice. A: Changes in body weight (BW) in WT and KRRki/ki mice that received intracerebroventricular administration of vehicle control (veh) or 2.5 µg FTY720 (FTY) twice a week (n = 6 per group). *P < 0.05, #P < 0.01 vs. KRRki/ki + vehicle. Evaluation of fat and lean mass by CT (B), body temperature (BT) (C), VO2 (D), locomotor activity (E), glucose tolerance test (F), PP2A and PP2B (calcineurin) activity in hypothalamus (G), and qRT-PCR analysis for genes consistent with beige adipocytes (I), and representative images of immunoblot analysis for p-AMPK and p-Akt in the hypothalami of WT and KRRki/ki mice treated with intracerebroventricular vehicle control or FTY for 14 days (H) (n = 5–7 per group). Quantification is shown. *P < 0.05, #P < 0.05 vs. KRRki/ki + vehicle. Data are represented as mean ± SEM.