Figure 5.
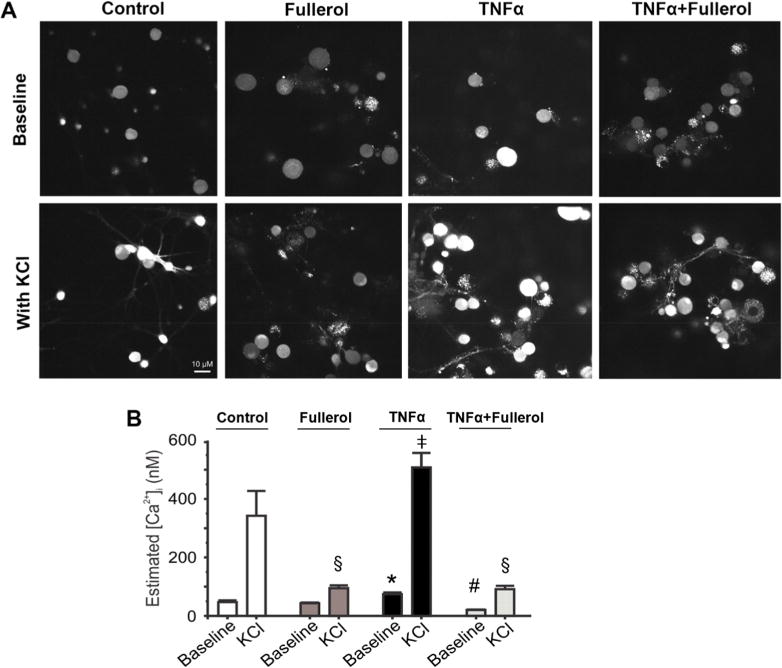
Fullerol abolishes the TNF-α-induced increase in [Ca2+]i in primary DRG neurons. (A) Representative images showing intracellular Ca2+ fluorescence of primary DRG neurons pretreated with F-12 media (control), fullerol (1 μM), TNF-α (10 ng/mL), or TNF-α (10 ng/mL) + fullerol (1 μM) overnight in the absence (upper row) or presence (lower row) of 60 mM KCl. (B) Nanofullerol neutralizes the increase in estimated intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) induced by TNF-α. Whereas neurons treated exclusively with TNF-α lead to higher [Ca2+]i, those treated with fullerol and TNF-α + fullerol show significantly lower global ([Ca2+]i). KCl-stimulated elevations in [Ca2+]i are also reduced by pretreating with fullerol. For baseline, p < 0.05, *TNF-α vs control, fullerol, and TNF-α + fullerol; #TNF-α + fullerol vs control, fullerol, and TNF-α. For KCl treated, p < 0.05, §Fullerol vs control; ‡TNF-α vs fullerol and TNF-α + fullerol. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; 20–30 neurons were analyzed per group.
