Figure 1.
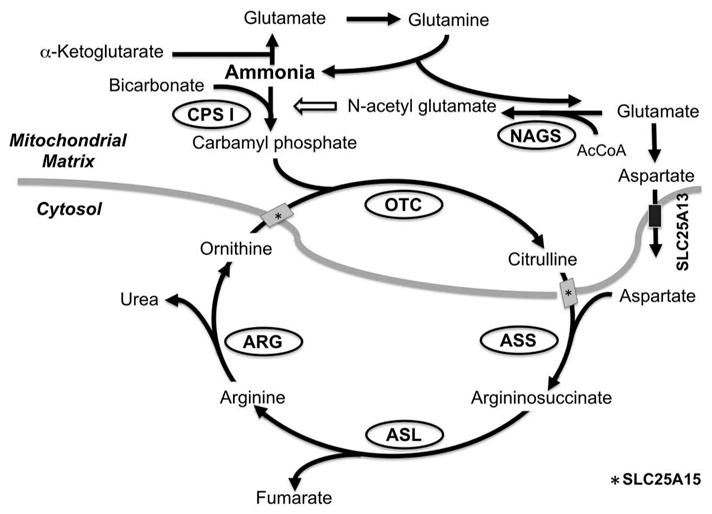
The urea cycle and the mechanism of action of N-carbamoyl-L-glutamic acid (NCG). The enzymes in ovals and the solute transporters depicted by rectangles comprise the urea cycle. Thick gray line depicts mitochondrial membranes. NCG is a synthetic analogue of N-acetylglutamate and activates Carbamoyl phosphate synthase I (CPS1) and enhance ureagenesis through the urea cycle. AcCoA: Acetyl CoA; ASL: Argininosuccinate lyase; ARG: Arginase; ASS: Argininosuccinic acid synthetase; CPS I: Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I; GPB: Glycerol phenylbutyrate; NAGS: N-acetylglutamate synthase; OTC: Ornithine transcarbamoylase; PAGN: Phenylacetylglutamine.
