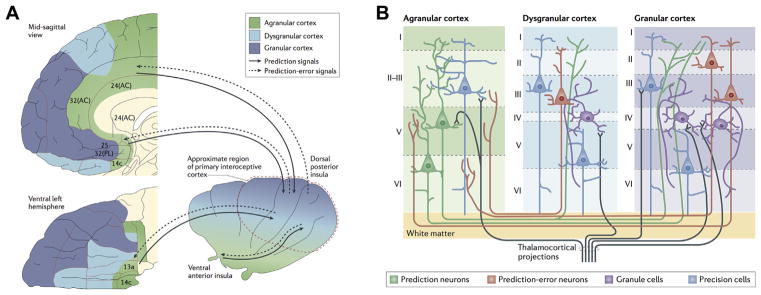
Figure 4.
(A) Active inference implementation according to the Embodied Predictive Interoception Coding model. Agranular visceromotor cortices, including the cingulate cortex, posterior ventral medial prefrontal cortex, posterior orbitofrontal cortex, and ventral anterior insula, estimate the balance among autonomic, metabolic, and immunological resources available to the body and its predicted requirements. These agranular visceromotor cortices issue allostatic predictions to hypothalamus, brainstem, and spinal cord nuclei to maintain a homeostatic internal milieu and simultaneously to the primary interoceptive sensory cortex in the mid and posterior insula. The interoceptive sensory cortex in the granular mid and posterior insula sends reciprocal prediction error signals back to the agranular visceromotor regions to modify the predictions. Under usual circumstances, these agranular regions are relatively insensitive to such feedback, which explains why interoceptive predictions are fairly stable in the face of body fluctuations. One hypothesis of the role of interoception in mental illness is that interoceptive input (i.e., posteriors) becomes increasingly decoupled from interoceptive predictions issued by the agranular visceromotor cortex (priors), leading to increased interoceptive prediction error signals. This decoupling may present in the brain as “noisy afferent interoceptive inputs” (97). (B) Proposed intracortical architecture and intercortical connectivity for interoceptive predictive coding. The granular cortex contains six cell layers including granule cells, which are excitatory neurons that amplify and distribute thalamocortical inputs throughout the column. The granular cortex is structurally similar to the neocortex and therefore more recently evolved than the agranular and dysgranular cortices. Within the insula, the granular cortex is present in the mid and posterior sectors. AC, anterior cingulate; PL, prelimbic cortex. [Figures reproduced, with permission, from Barrett and Simmons (45).]