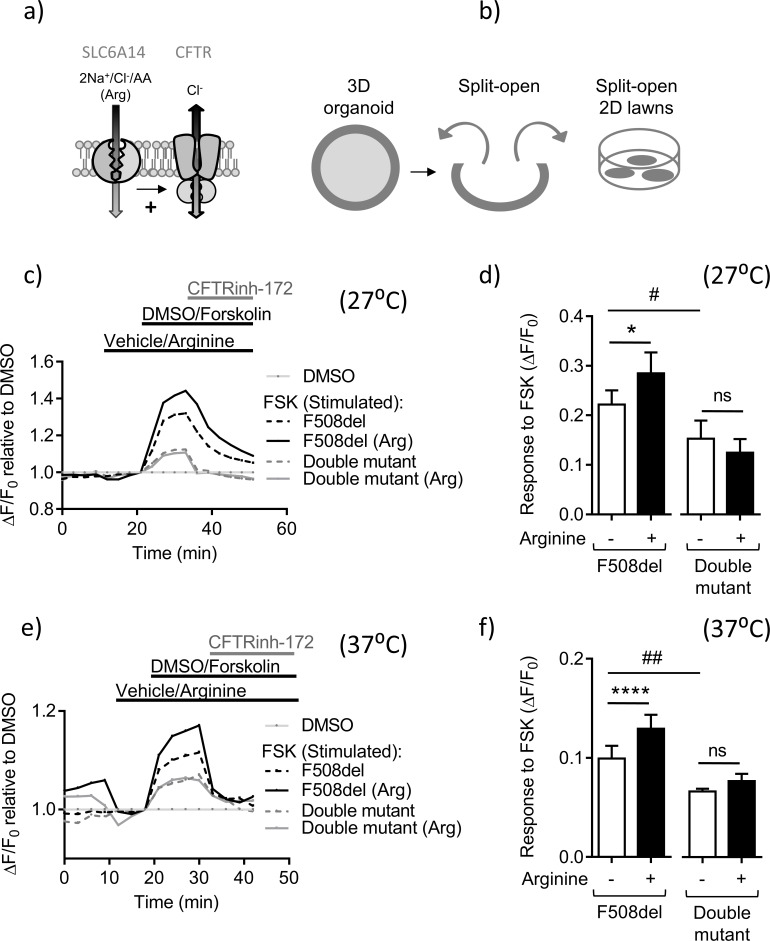
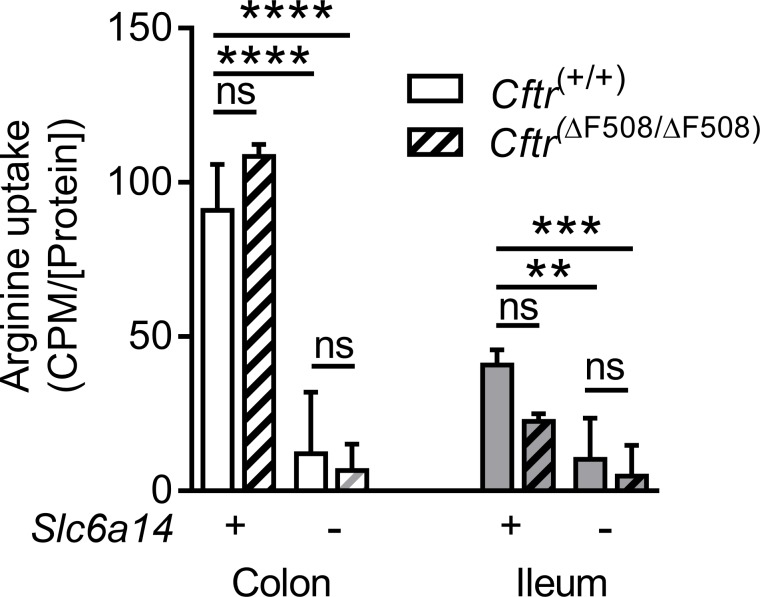
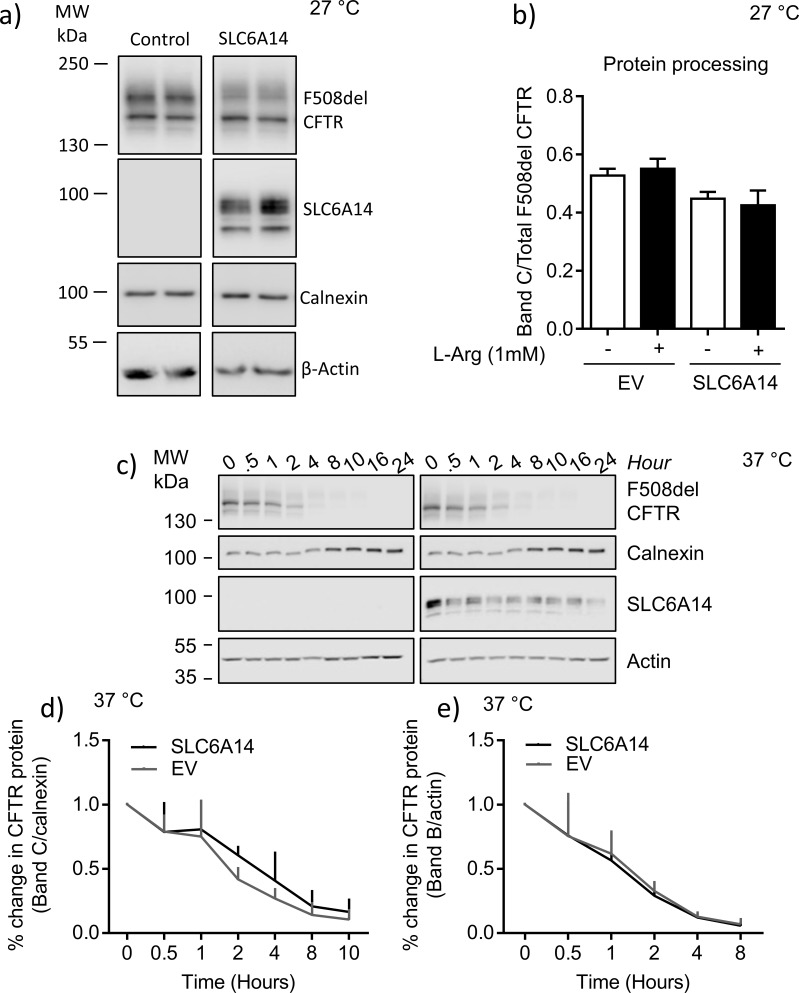
Figure 5. Slc6a14 expression mediates arginine-dependent enhancement of mutant F508del CFTR channel function in murine intestinal tissues.
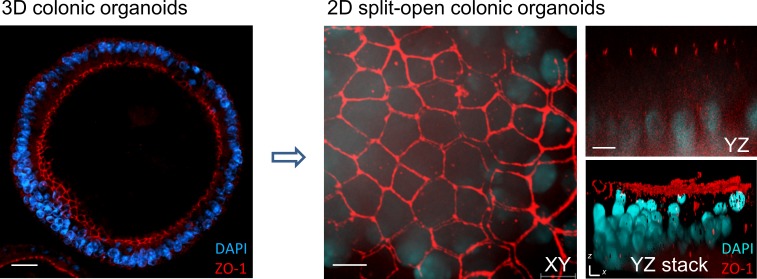
(a) Hypothetical model depicting that SLC6A14 could affect CFTR channel function. (b) Diagram depicts the concept of gaining apical access to the epithelium by splitting open a 3D organoid, thereby resulting in patches of split-open 2D lawns, which can then be studied using fluorescence-based assays. (c) Split-open colonic organoids from CF (CftrF508del/F508del) and double mutant (CftrF508del/F508del; Slc6a14(-/y)) mice were studied for CFTR channel function using the previously described membrane potential-based ACC assay. Line graph represents change in fluorescence relative to baseline (ΔF/F0) as a measure of F508del-CFTR function after low temperature rescue (27°C) of the mutant protein. After capturing baseline fluorescence reads, cells were acutely treated with L-arginine (1 mM) to activate SLC6A14 or vehicle, followed by CFTR activation with cAMP agonist forskolin (FSK 10 µM) or vehicle DMSO. Thereafter, CFTRinh-172 (10 µM) was added to all the wells. (d) Bar graph represents maximum change in ACC fluorescence from baseline (ΔF/F0) after acute addition of FSK, following low temperature (27°C) rescue of F508del-CFTR protein in split-open murine organoids (mean ± SEM). Paired t-test was performed (*p=0.045, ns = not significant, n = 4 mice for each genotype). (e) ACC assay performed on split-open colonic organoids from CF (CftrF508del/F508del) and double mutant (CftrF508del/F508del; Slc6a14(-/y)) mice for CFTR channel function at physiological temperature (37°C). As above, SLC6A14 was activated with L-arginine (1 mM) or vehicle followed by CFTR stimulation by FSK (10 µM) or vehicle DMSO. All wells received CFTRinh-172 (10 µM) after activation to confirm the role for CFTR. (f) Bar graph represents maximum change in ACC fluorescence from baseline (ΔF/F0) after acute addition of FSK, at physiological temperature (37°C) in F508del-CFTR split-open murine organoids (mean ± SEM). Paired t-test was performed (****p<0.0001, ns = not significant, n = 3 mice for each genotype).