Extended Data Figure 4. Replication of previous association between JAK2 46/1 haplotype and 9p CNN-LOH in cis due to clonal selection.
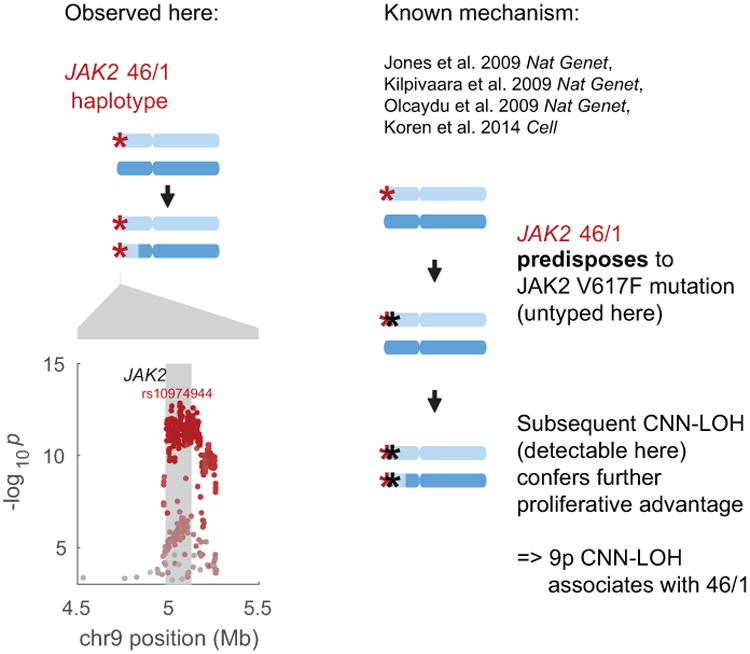
The common JAK2 46/1 haplotype has previously been shown to confer risk of somatic JAK2 V617F mutation such that subsequent 9p CNN-LOH produces a strong proliferative advantage15-18,20 (right side of figure). In our analysis, CNN-LOH on 9p is strongly associated with JAK2 46/1 (P=1.6×10−13, OR = 2.7 (2.1–3.5); Fisher's exact test on n=120,664 individuals) with the risk haplotype predominantly duplicated by CNN-LOH in hets (52 of n=61 heterozygous cases; binomial P=1.8×10−8). In the left side of this figure, the genomic modification is illustrated in the top panel and association signals are plotted in the bottom. The lead associated variant is labeled, and variants are colored according to linkage disequilibrium with the lead variant (scaled for readability).
