Fig. 1.
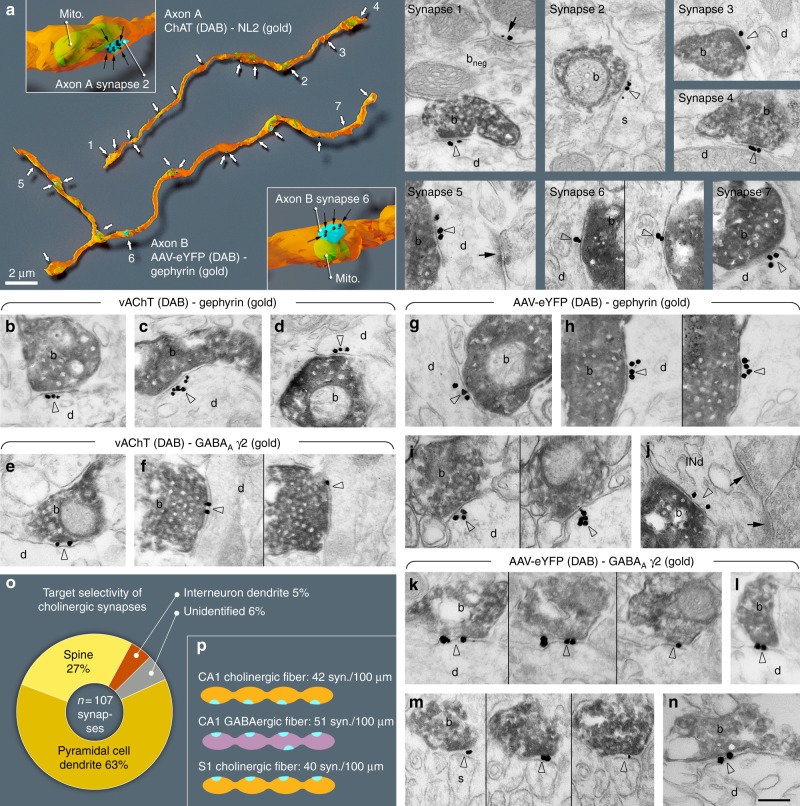
All cholinergic terminals establish synapses, express GABAergic markers and innervate pyramidal cells or interneurons. a Three-dimensional EM reconstructions show that hippocampal cholinergic fibres form synapses (arrows) frequently. Axon A is labelled for ChAT in a WT mouse. Axon B is an AAV-eYFP virus-labelled septo-hippocampal fibre in a ChAT-Cre mouse. Insets show two typical terminals with synapses (blue). The plasma membrane was made partially transparent to reveal mitochondria (mito, green). Gold labellings of NL2 (axon A, synapse 1–4) or gephyrin (axon B, synapse 5–7) were used to recognise synapses (black dots and arrows in the insets). EM images show terminal boutons (b) of the reconstructed axonal segments establishing synapses 1–7 (arrowheads, indicated by the same numbers on the left) on dendrites (d) and a spine (s). Next to synapse 1, a ChAT-negative, putative GABAergic terminal bouton (bneg) forming a NL2-positive synapse (arrow) is also shown. b–n EM images reveal the presence of gephyrin (arrowheads, gold; b–d; g–j) and GABAA γ2 receptor subunits (arrowheads, gold; e–f; k–n) postsynaptically in synapses established by vAChT-positive terminals in WT mice (b–f; DAB, b) or by AAV-eYFP-labelled septo-hippocampal terminals in ChAT-Cre mice (g–n; DAB, b). Images of consecutive sections are separated by thin black lines. Terminals innervate dendrites (d) or spines (s). In j, the postsynaptic target is an interneuron dendrite (INd) that receives type-I synapses as well (arrows). Synapses are from str. ori. (a, b–e, g–j, l, m), str. rad. (k, n) and str. l-m (f). Scale bar is 200 nm for all EM images. o Postsynaptic target selectivity of reconstructed cholinergic axonal segments from str. oriens and radiatum. Spine: 27.1%, pyramidal cell dendrite: 62.6%, interneuron dendrite: 4.7%, unidentifiable: 5.6%. p Comparison of the number of synapses per 100 µm cholinergic axonal segments in CA1 and S1 cortex and GABAergic fibres in CA1