Figure 1.
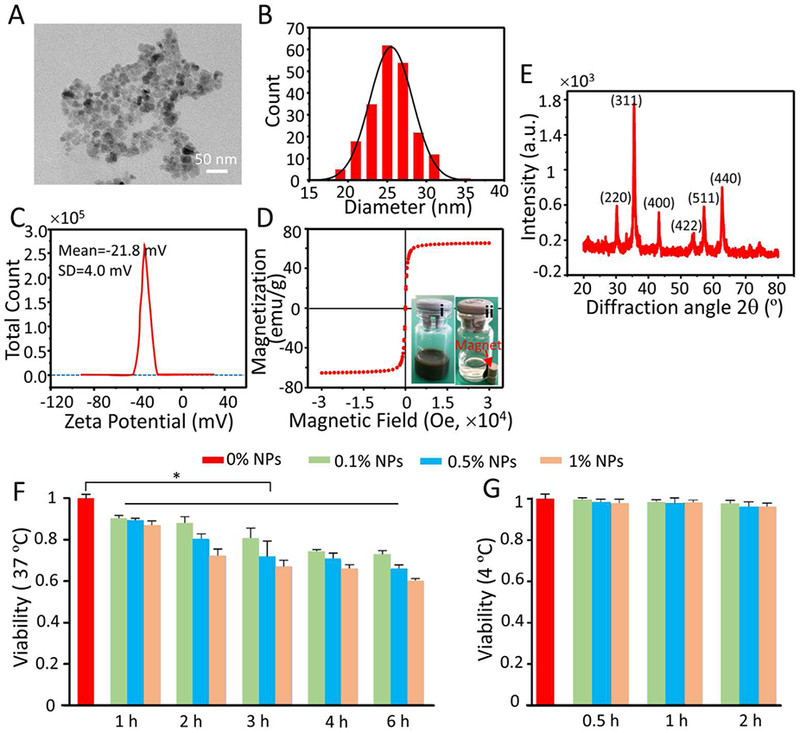
Characterization and cytotoxicity of Fe3O4 NPs. A) Representative TEM images of Fe3O4 NPs. B) Size distribution of Fe3O4 NPs quantified by dynamic light scattering (DLS) at room temperature. C) Zeta potential of Fe3O4 NPs measured at room temperature. D) Magnetization curve of Fe3O4 NPs quantified by superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) at room temperature. The insets (i) and (ii) show typical images of the Fe3O4 NPs dispersed in deionized water before and after applying magnetic field using a magnet, respectively. E) X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern of Fe3O4 NPs. F-G) Cytotoxicity of the Fe3O4 NPs detected by the CCK-8 assay at 37 °C (F) and 4 °C (G) after different incubation times. Time- (1, 2, 3, 4, and 6 h) and concentration-dependent (0.1, 0.5, and 1% (w/v)) cytotoxicity was observed at 37 °C, but no cytotoxicity was observed after the cells were treated with different concentrations (0.1, 0.5, and 1% (w/v)) of NPs for 0.5, 1, and 2 h at 4 °C.
