Figure 5.
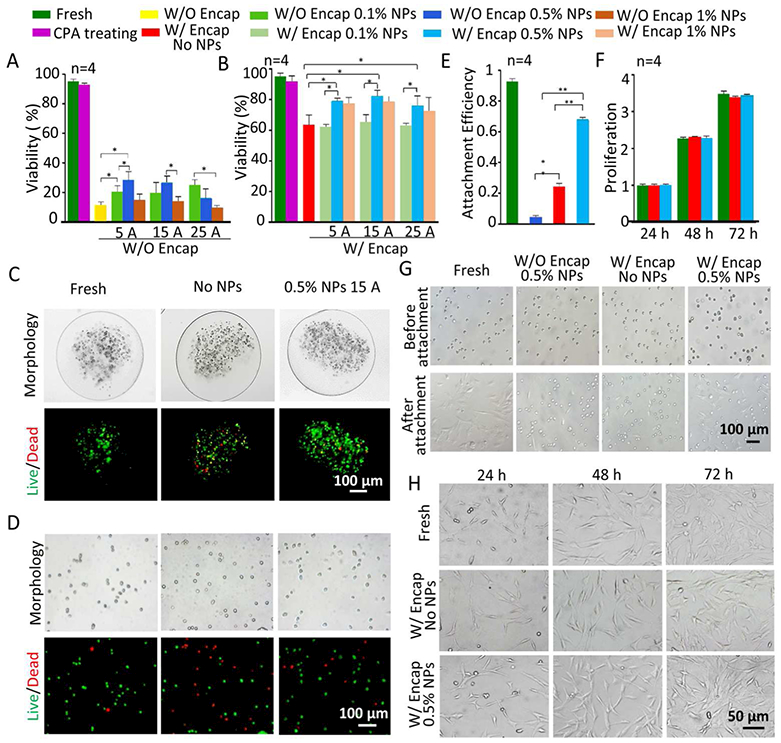
Cell viability, attachment efficiency, and proliferation of pADSCs post-vitrification under different conditions. Viability of non-encapsulated pADSCs (A) and encapsulated pADSCs (B) under different conditions, i.e., fresh, CPA treated, and post-vitrification without or with three different concentrations of NPs with nano-warming by MIH under an AC magnetic field (5 A, 15 A and 25 A). C) Typical DIC and fluorescence images show the morphology and viability of pADSCs in microcapsules under three different conditions, i.e., fresh and post-cryopreservation without NPs and with 0.5% NPs with nano-warming by MIH under an AC magnetic field (15A). D) Typical DIC and fluorescence images showing the morphology and viability of pADSCs released from microcapsules post-vitrification under the same three conditions in (C). E) The attachment efficiency of non-encapsulated and microencapsulated pADSCs post-vitrification with or without nano-warming by MIH of 0.5% Fe3O4 NPs (15 A). F) The proliferation of microencapsulated pADSCs post-vitrification without or with nano-warming by MIH of 0.5% Fe3O4 NPs (15 A). G) Representative images of pADSC attachment under the aforementioned conditions. H) Representative images of pADSC proliferation under different conditions. Red: dead and green: live. *: p < 0.05. **: p < 0.01. W/O Encap: without encapsulation and W/ Encap: with encapsulation.
