Figure 4.
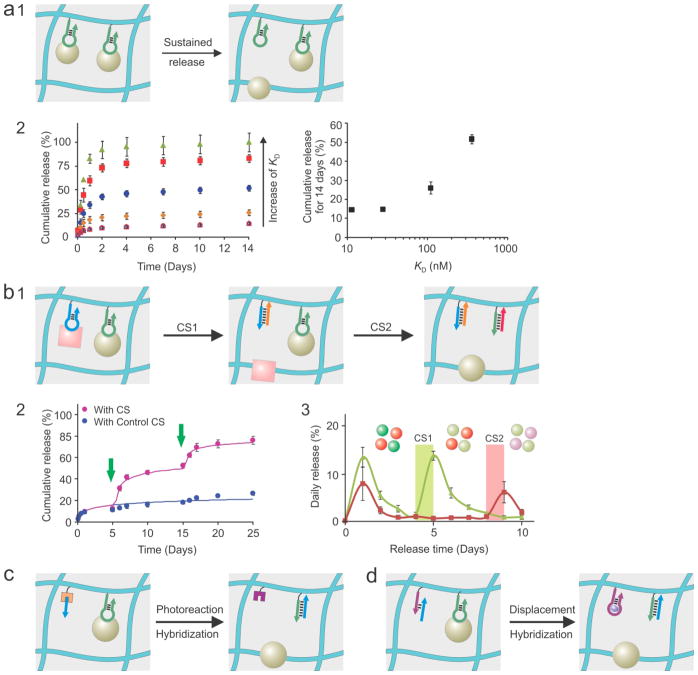
Aptamers as pendent groups for sustained and programmed protein release from hydrogels. (a) Protein dissociation for sustained release. a1: schematic illustration; a2: experimental results. Adapted from refs. 25 and 29 with permission. (b) Sequential release of single or multiple proteins. CS: complementary sequence. Aptamers can not only bind target proteins but also sense their triggering CSs. b1: schematic illustration; b2: Release of one protein for two times (green arrow: CS triggering); b3: programmed release of two proteins. Adapted from refs. 27 and 28 with permission. (c) Integration of external (e.g., light) and internal triggers for self-programmed protein release. Adapted from ref. 137 with permission. (d) Integration of two internal triggers for metabolite-regulated self-programmed protein release. Two aptamers are used in this hydrogel system. One (green arrow) binds the target protein and senses the triggering CS (blue arrow). The other (purple arrow) senses the metabolite for triggering initiation of the protein-bound aptamer. Adapted from ref. 59 with permission.