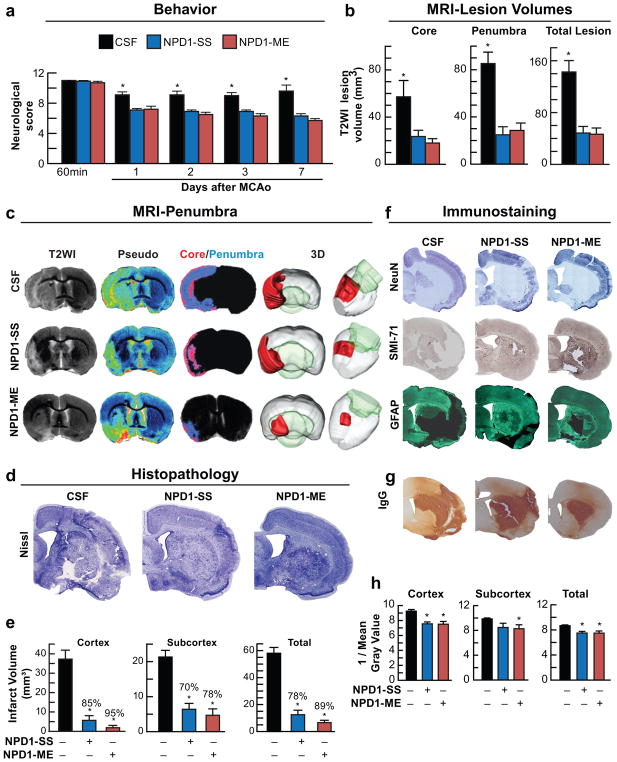
Fig. 7.
Neuroprotectin D1 (NPD1) promotes motor functional recovery, protects the penumbra, reduces MRI lesion volumes, attenuates cell damage and diminishes neurovascular unit (NVU) disruption one week after ischemic stroke. Rats were subjected to 2h of MCAo, NPD1-SS, NPD1-ME (as sodium salts or methyl esters; 5μg/per rat) or CSF were administered into lateral cerebral ventricle at 3h after onset of stroke. (a) Total neurological score during 7 days survival period; (b) Ischemic core, penumbra and total lesion volumes computed from T2WI images on day 7; (c) Representative T2WI, pseudo-images, core/penumbra and 3D lesion volumes computed from T2WI on day 7. Core and penumbra were extracted from the entire brain. Core (red) and penumbral (blue) tissues were automatically identified in vehicle- and NPD1-treated animals using the computational MRI method, Hierarchal Region Splitting, for penumbra identification. (d) Representative Nissl stained brain sections from rats treated with CSF, NPD1-SS and NPD1-ME. (e) Cortical, subcortical and total infarct volumes from all groups. (f) Representative NeuN (blue), SMI-71 (brown) and GFAP (dark green) stained brain sections from all groups. (g) NVU breakdown was assessed by immunodetection of immunoglobulin G (IgG) within the parenchyma. IgG staining (brown) indicating NVU breakdown. (h) Bar graph shows that NPD1-SS and NPD1-ME significantly reduced IgG immunoreactivity in cortex, subcortex and whole right hemisphere (total). Values shown are means ± SD (n=5–6 per group). *p<0.05, versus the vehicle group (repeated measures ANOVA followed by Bonferroni tests)