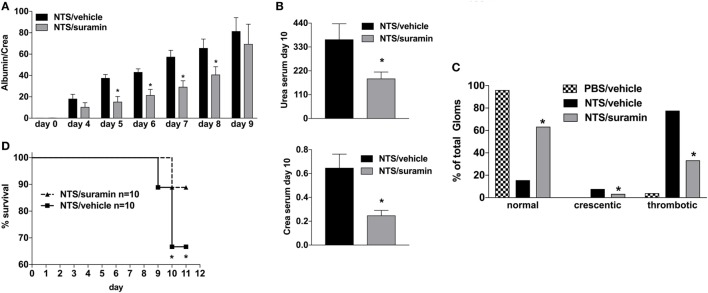
Figure 3.
Effect of P2R-antagonist Suramin treatment on nephrotoxic serum (NTS)-driven glomerulonephritis (GN). C57BL/6 mice received either vehicle (PBS) or NTS (solved in PBS) intravenous on days 1, 2, and 3 to induce GN. For treatment, they received i.p. injections of either vehicle or suramin (100 µM in 100 µl) on days 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9. Urine was collected daily and analyzed for its albumin–creatinine quotient (A). Animals were killed on day 10 after a blood sample had been taken. This was analyzed for its serum urea and creatinine levels (B). From the killed animals, kidney tissue was prepared and analyzed with microscopy (PAS-staining). Approximately 100 Glomerula in each sample were analyzed following the histological criteria “normal, crescentic, or thrombotic” (C). Follow-up of mice receiving apyrase or vehicle are shown (D). Data are shown as mean ± SEM, n = 4–5 mice in each group. *P < 0.05. Data from one representative experiment out of three are shown.